Subcool Superheat Chart
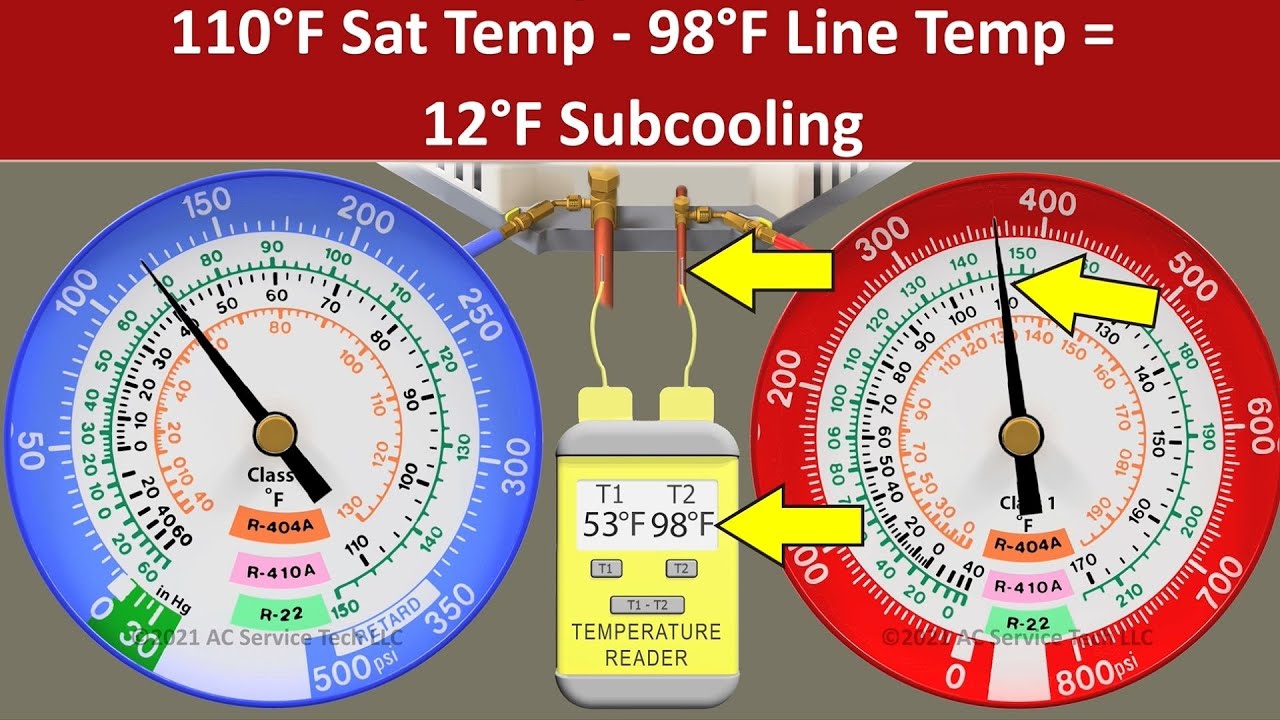
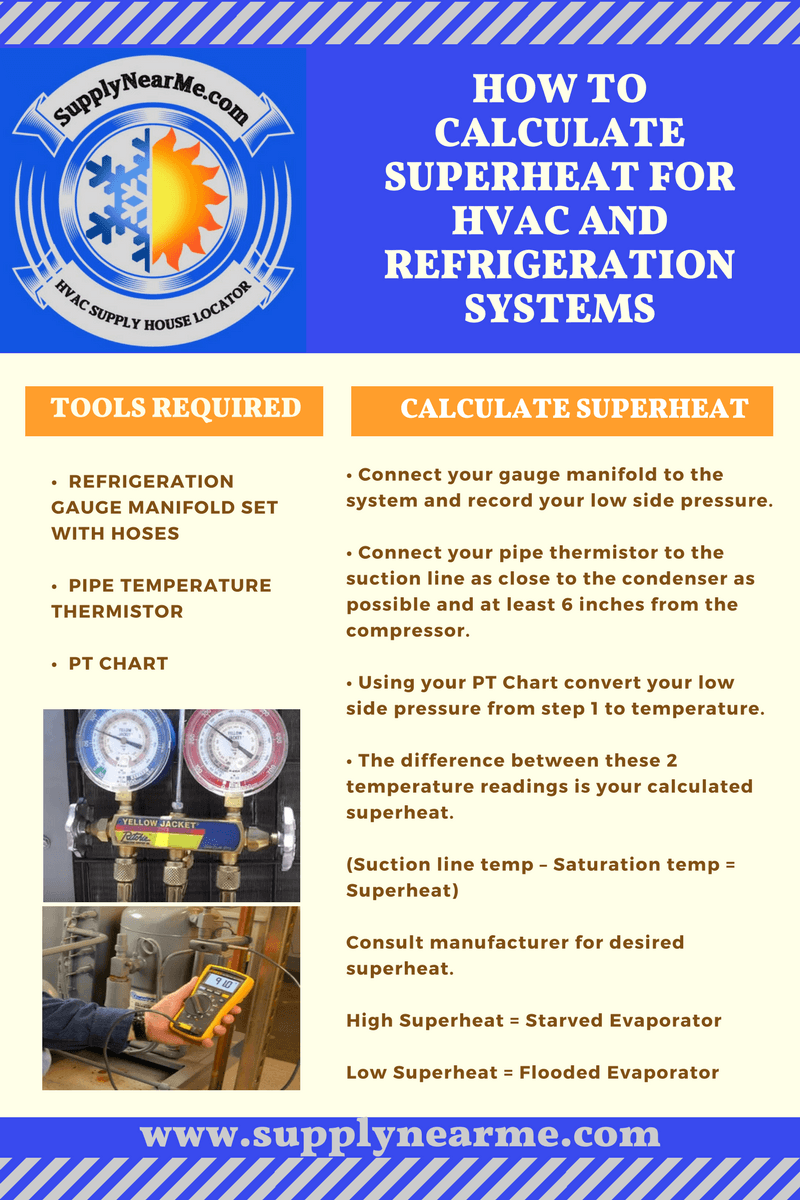
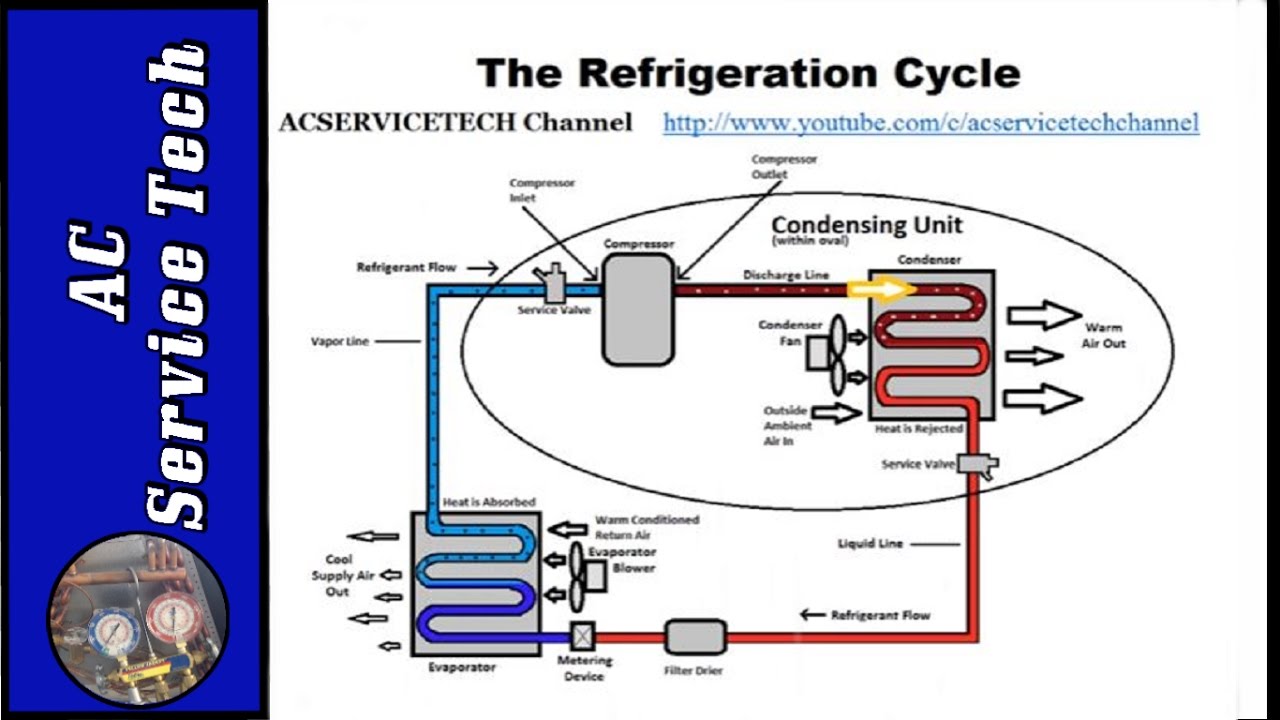
Subcool Superheat Chart - Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Web you can use refrigerant pressure/temperature (p/t) charts or temperature scales on analog gauges to show the relationship between refrigerant pressure and saturation temperature. This is the refrigerant temperature decrease in the outdoor unit (condenser coil). Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor. A decrease in liquid temperature (suction line). For superheat or low side pt data. Web superheat and subcooling troubleshooting chart. How to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling. Match low side manifold gauge reading (suction pressure) “super heat” 4. At 212º f there is both liquid and. Find out what it means when your system has normal subcooling but high superheat, and learn how to diagnose and resolve this issue. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). A decrease in liquid temperature (suction line). Ensure proper temperature clamp location. Use the refrigerant pressure/temperature chart to convert the pressure reading to the condenser saturation temperature. Superheat is defined as the amount of heat added to a vapor above its boiling point. Web superheat/subcooling calculator with thermometer and p/t chart (69196) operating steps. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Web superheat determines by how many degrees of temperature refrigerant vapor increases in the system. Web measure the condenser pressure at the service valve by reading the pressure on the refrigerant manifold gauges. Web superheat determines by how many degrees of temperature refrigerant vapor increases in the system. Web what are superheat and subcooling? To calculate superheat and subcooling measurements, a specific mathematical chart is used, and the process is mostly done by an hvac technician. Web hvac app to calculate subcooling. Web superheat and subcooling troubleshooting chart. Find out what it means when your system has normal subcooling but high superheat, and learn how to diagnose and resolve this issue. Web when charging a fixed orifice a/c system, you can use the chart below to figure out the proper superheat to set once all other parameters have been accounted for. Find leaks, seal and recharge. Web what. Superheat is defined as the amount of heat added to a vapor above its boiling point. Web what are superheat and subcooling? Web hvac app to calculate subcooling. Web superheat measures the freon boiling point in gas form while subcooling measures the freon in liquid form below the evaporation level. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available. For superheat or low side pt data. Web when charging a fixed orifice a/c system, you can use the chart below to figure out the proper superheat to set once all other parameters have been accounted for. Pay attention to it because you will need the saturation temperature to determine superheat and subcooling. Use the refrigerant drop down for access. Web superheat measures the freon boiling point in gas form while subcooling measures the freon in liquid form below the evaporation level. Subcooling is quite the reverse to superheat. We are usually looking for 7°f to 15°f superheat. Web superheat and subcooling troubleshooting chart. Web working with 410a refrigerant? Find out what it means when your system has normal subcooling but high superheat, and learn how to diagnose and resolve this issue. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; We will show you exactly how to measure the superheat for any air conditioner. Low refrigerant charge on liquid and suction line. At 212º. Web working with 410a refrigerant? A system with a fixed metering device must be charged by superheat. Web superheat/subcooling calculator with thermometer and p/t chart (69196) operating steps. Web measure the condenser pressure at the service valve by reading the pressure on the refrigerant manifold gauges. Let's use water as an example to show what is going on. Match low side manifold gauge reading (suction pressure) “super heat” 4. Web superheat and subcooling troubleshooting chart. Here is what we know. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Subcooling is quite the reverse to superheat. At 212º f there is both liquid and. Web superheat determines by how many degrees of temperature refrigerant vapor increases in the system. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Alternatively, you can use our special superheat and delta t calculator here (top left). This is the refrigerant temperature decrease in the outdoor unit (condenser coil). Pay attention to it because you will need the saturation temperature to determine superheat and subcooling. To calculate superheat and subcooling measurements, a specific mathematical chart is used, and the process is mostly done by an hvac technician. Low refrigerant charge on liquid and suction line. For superheat or low side pt data. Web hvac app to calculate superheat. Web measure the condenser pressure at the service valve by reading the pressure on the refrigerant manifold gauges. Web hvac app to calculate subcooling. Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. S ubcooling is defined as the amount of heat removed from a liquid below its condensing point. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Find out what it means when your system has normal subcooling but high superheat, and learn how to diagnose and resolve this issue. How to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling. Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor. Use the and to display the desired refrigerant. Web what are superheat and subcooling? Let's use water as an example to show what is going on. Pay attention to it because you will need the saturation temperature to determine superheat and subcooling. Alternatively, you can use our special superheat and delta t calculator here (top left). Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Ensure proper temperature clamp location. Match low side manifold gauge reading (suction pressure) “super heat” 4.Subcool And Superheat Chart
Printable Superheat And Subcooling Chart
Superheat And Subcooling Chart
Superheat And Subcooling Troubleshooting Chart
Superheat And Subcool Chart
Superheat And Subcooling Chart
Hvac Superheat And Subcooling Chart Labb by AG
Superheat And Subcooling Chart 410a
Superheat And Subcooling Troubleshooting Chart
Superheat And Subcool Chart
In This Article, You Will Similarly Get 3 Key Resources That Will Explain Everything To Know About Subcooling Calculation, Including:
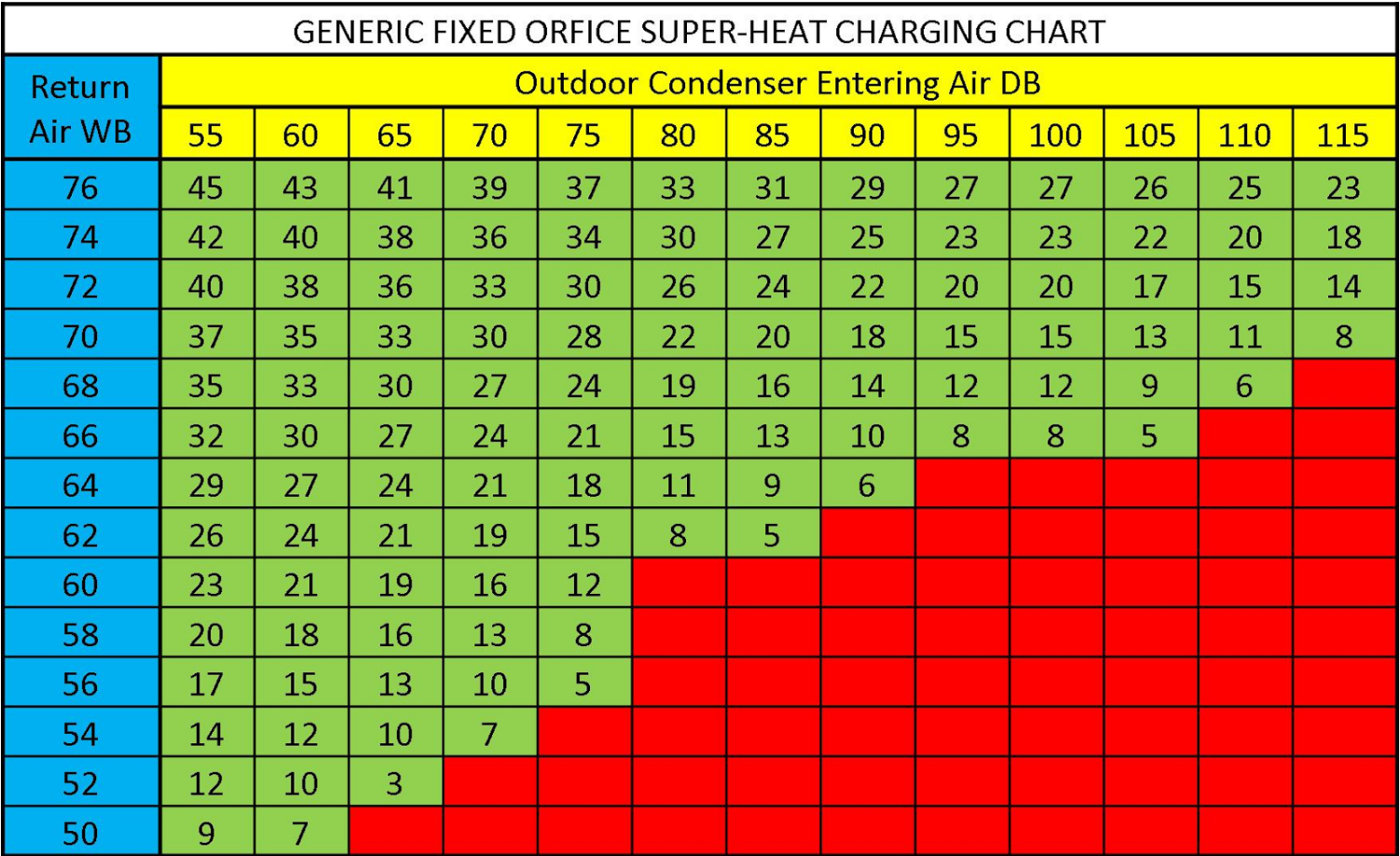
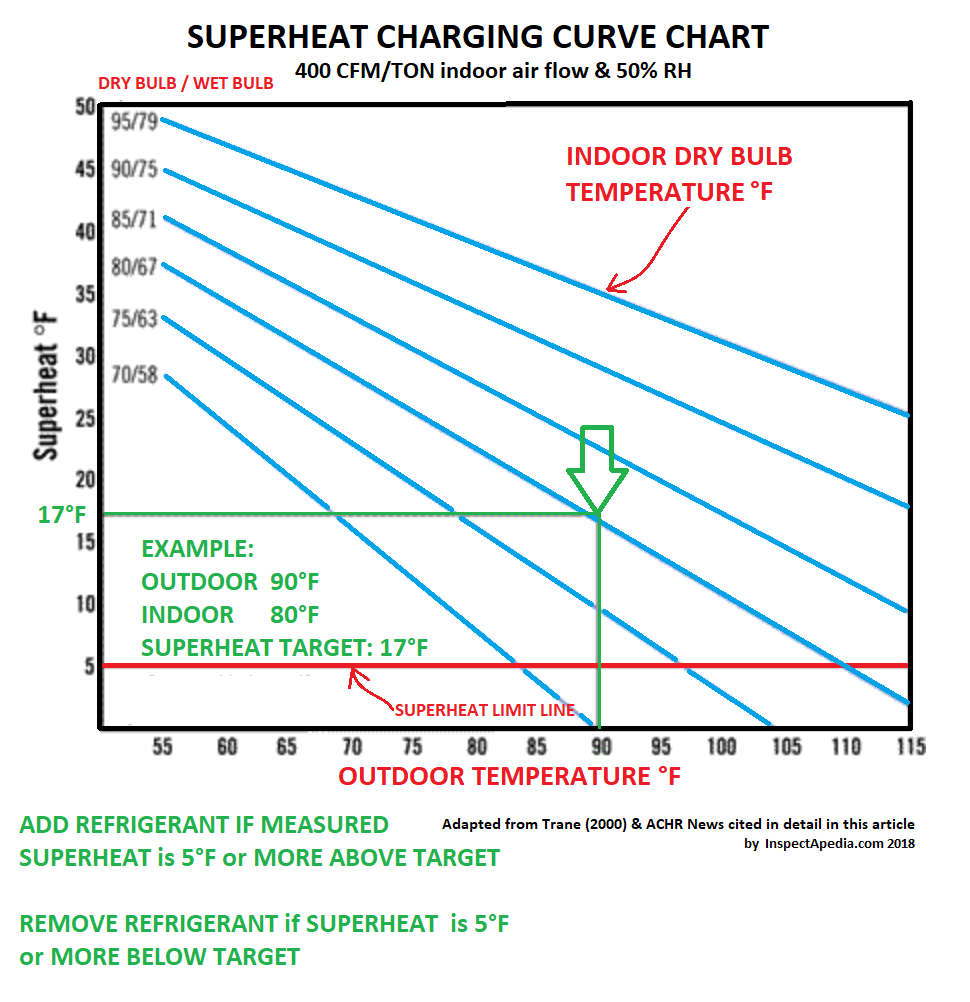
Web When Charging A Fixed Orifice A/C System, You Can Use The Chart Below To Figure Out The Proper Superheat To Set Once All Other Parameters Have Been Accounted For.
Easy Way To Remember What Superheat Is:
Measuring Superheat Is Not All That Difficult.
Related Post: