Inop Equipment Flow Chart
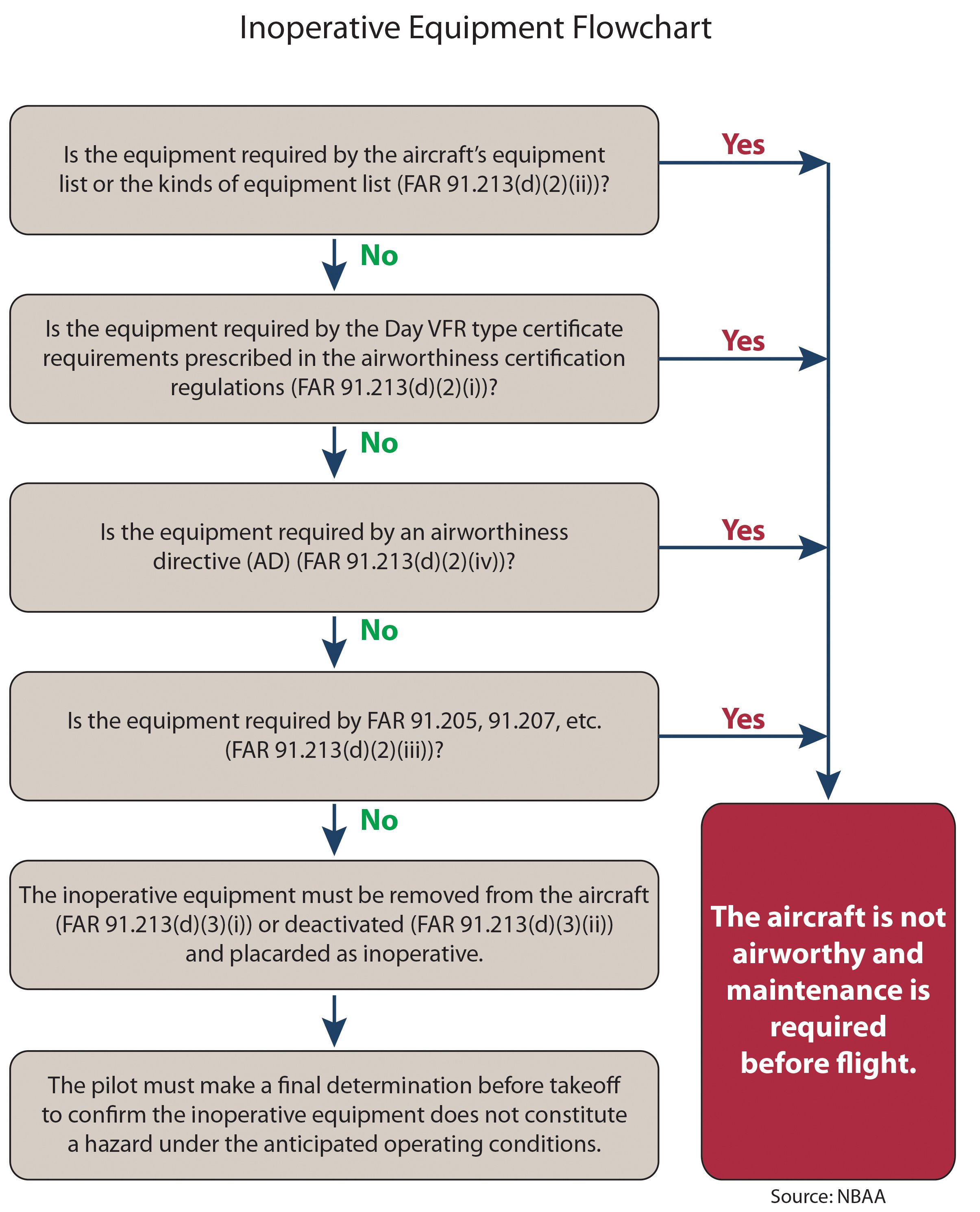
Inop Equipment Flow Chart - This table applies to approach inoperative, each minimum is raised to the highest minimum required by any single component that is inoperative. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. Web an aircraft with inoperative instruments or equipment as provided in paragraph (d) of this section is considered to be in a properly altered condition acceptable to the administrator. Web dealing with inoperative equipment is a challenge for both new and experienced pilots alike. Web (1) instruments and equipment that are either specifically or otherwise required by the airworthiness requirements under which the aircraft is type certificated and which are essential for safe operations under all operating conditions. This infographic helps break down 91.213. Operation of aircraft with a minimum equipment list (mel), as authorized by far 6 91.213(a). Web this advisory circular (ac) describes acceptable methods for the operationof aircraft under federal aviation regulations (far) part 91 with certain inoperative instruments and equipment which are not essential for safe flight. Web the foremost importance of inoperative equipment flow charts lies in their role in ensuring flight safety. The mel is intended to permit operations with inoperative items of equipment for the minimum period of time necessary until repairs can be accomplished. Web an aircraft with inoperative instruments or equipment as provided in paragraph (d) of this section is considered to be in a properly altered condition acceptable to the administrator. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. The main regulation is far 91.213, helpfully titled “inoperative instruments and equipment.” Operation of aircraft with a minimum equipment list (mel), as authorized by far 6 91.213(a). The mel is intended to permit operations with inoperative items of equipment for the minimum period of time necessary until repairs can be accomplished. This table applies to approach inoperative, each minimum is raised to the highest minimum required by any single component that is inoperative. This infographic helps break down 91.213. Web dealing with inoperative equipment is a challenge for both new and experienced pilots alike. Web per the flowchart, the first step is determining if the inoperative equipment appears in the aircraft’s equipment list or koel (kinds of equipment list) per… “section 91.213(d)(2)(ii).” incidentally, references to 91.213(d)(2) (i) , (ii) , (iii) and (iv) appear throughout this particular document. Web inoperative minimums are published on the instrument approach charts as localizer minimums. This infographic helps break down 91.213. Web inoperative minimums are published on the instrument approach charts as localizer minimums. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. Web (1) instruments and equipment that are either specifically or otherwise required by the airworthiness requirements under which the aircraft. Web (1) instruments and equipment that are either specifically or otherwise required by the airworthiness requirements under which the aircraft is type certificated and which are essential for safe operations under all operating conditions. Web an mel allows an operator to continue to operate an aircraft with certain inoperative items or to reposition the aircraft to a place where repairs. Web this advisory circular (ac) describes acceptable methods for the operationof aircraft under federal aviation regulations (far) part 91 with certain inoperative instruments and equipment which are not essential for safe flight. Web dealing with inoperative equipment is a challenge for both new and experienced pilots alike. There are three regulations you need to review when using it. Web inoperative. The main regulation is far 91.213, helpfully titled “inoperative instruments and equipment.” This infographic helps break down 91.213. Web (1) instruments and equipment that are either specifically or otherwise required by the airworthiness requirements under which the aircraft is type certificated and which are essential for safe operations under all operating conditions. The mel is intended to permit operations with. Web this advisory circular (ac) describes acceptable methods for the operationof aircraft under federal aviation regulations (far) part 91 with certain inoperative instruments and equipment which are not essential for safe flight. The mel is intended to permit operations with inoperative items of equipment for the minimum period of time necessary until repairs can be accomplished. Web the foremost importance. There are three regulations you need to review when using it. This infographic helps break down 91.213. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. This table applies to approach inoperative, each minimum is raised to the highest minimum required by any single component that is inoperative.. The main regulation is far 91.213, helpfully titled “inoperative instruments and equipment.” There are three regulations you need to review when using it. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. Web an mel allows an operator to continue to operate an aircraft with certain inoperative items. Web inoperative minimums are published on the instrument approach charts as localizer minimums. Web per the flowchart, the first step is determining if the inoperative equipment appears in the aircraft’s equipment list or koel (kinds of equipment list) per… “section 91.213(d)(2)(ii).” incidentally, references to 91.213(d)(2) (i) , (ii) , (iii) and (iv) appear throughout this particular document. This infographic helps. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. Web an mel allows an operator to continue to operate an aircraft with certain inoperative items or to reposition the aircraft to a place where repairs can be made. Web the foremost importance of inoperative equipment flow charts lies. Operation of aircraft with a minimum equipment list (mel), as authorized by far 6 91.213(a). This table applies to approach inoperative, each minimum is raised to the highest minimum required by any single component that is inoperative. Web inoperative minimums are published on the instrument approach charts as localizer minimums. Web per the flowchart, the first step is determining if. Web an mel allows an operator to continue to operate an aircraft with certain inoperative items or to reposition the aircraft to a place where repairs can be made. Web an aircraft with inoperative instruments or equipment as provided in paragraph (d) of this section is considered to be in a properly altered condition acceptable to the administrator. Web dealing with inoperative equipment is a challenge for both new and experienced pilots alike. Web inoperative minimums are published on the instrument approach charts as localizer minimums. This infographic helps break down 91.213. Web this advisory circular (ac) describes acceptable methods for the operationof aircraft under federal aviation regulations (far) part 91 with certain inoperative instruments and equipment which are not essential for safe flight. There are three regulations you need to review when using it. Web the foremost importance of inoperative equipment flow charts lies in their role in ensuring flight safety. Web the flowchart on the opposite page describes the overall process for determining whether the airplane is airworthy despite failed equipment. Web (1) instruments and equipment that are either specifically or otherwise required by the airworthiness requirements under which the aircraft is type certificated and which are essential for safe operations under all operating conditions. Web per the flowchart, the first step is determining if the inoperative equipment appears in the aircraft’s equipment list or koel (kinds of equipment list) per… “section 91.213(d)(2)(ii).” incidentally, references to 91.213(d)(2) (i) , (ii) , (iii) and (iv) appear throughout this particular document. This table applies to approach inoperative, each minimum is raised to the highest minimum required by any single component that is inoperative.Inop Equipment Airline Pilot Central Forums
Inoperative Equipment Flow Chart
Inop Equipment Flow Chart
Inoperative Equipment Flow Chart
91.213 Inoperative Equipment Flow Chart r/flying
Airworthiness Inoperative Equipment Aeronautical Knowledge
Inoperative Equipment Flow Chart
Inop Equipment Flow Chart
Good To Go? Aviation Safety
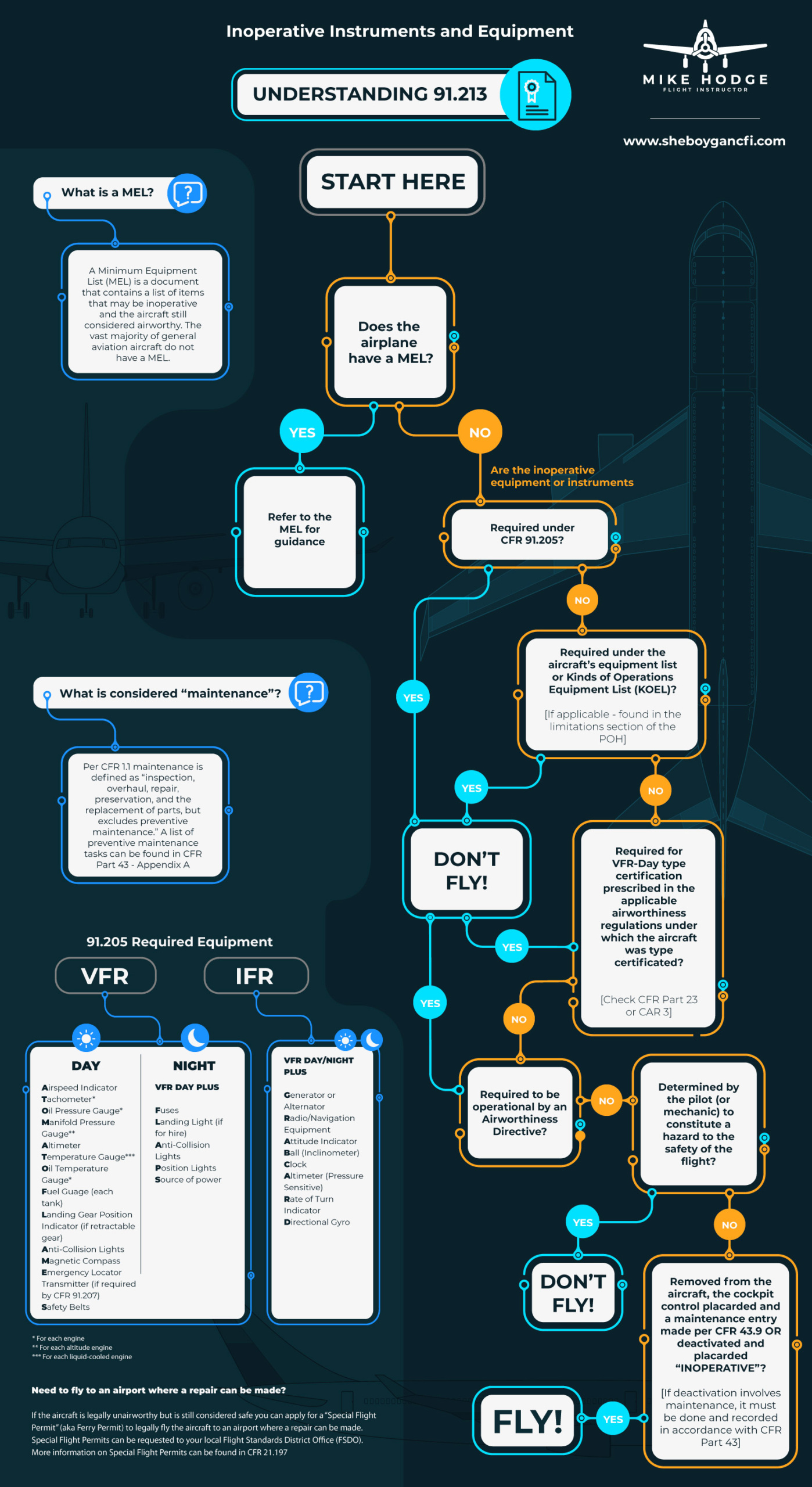
Understanding 91.213 Inoperative Equipment and Instruments
The Main Regulation Is Far 91.213, Helpfully Titled “Inoperative Instruments And Equipment.”
The Mel Is Intended To Permit Operations With Inoperative Items Of Equipment For The Minimum Period Of Time Necessary Until Repairs Can Be Accomplished.
Operation Of Aircraft With A Minimum Equipment List (Mel), As Authorized By Far 6 91.213(A).
Related Post: