Igneous Rock Chart
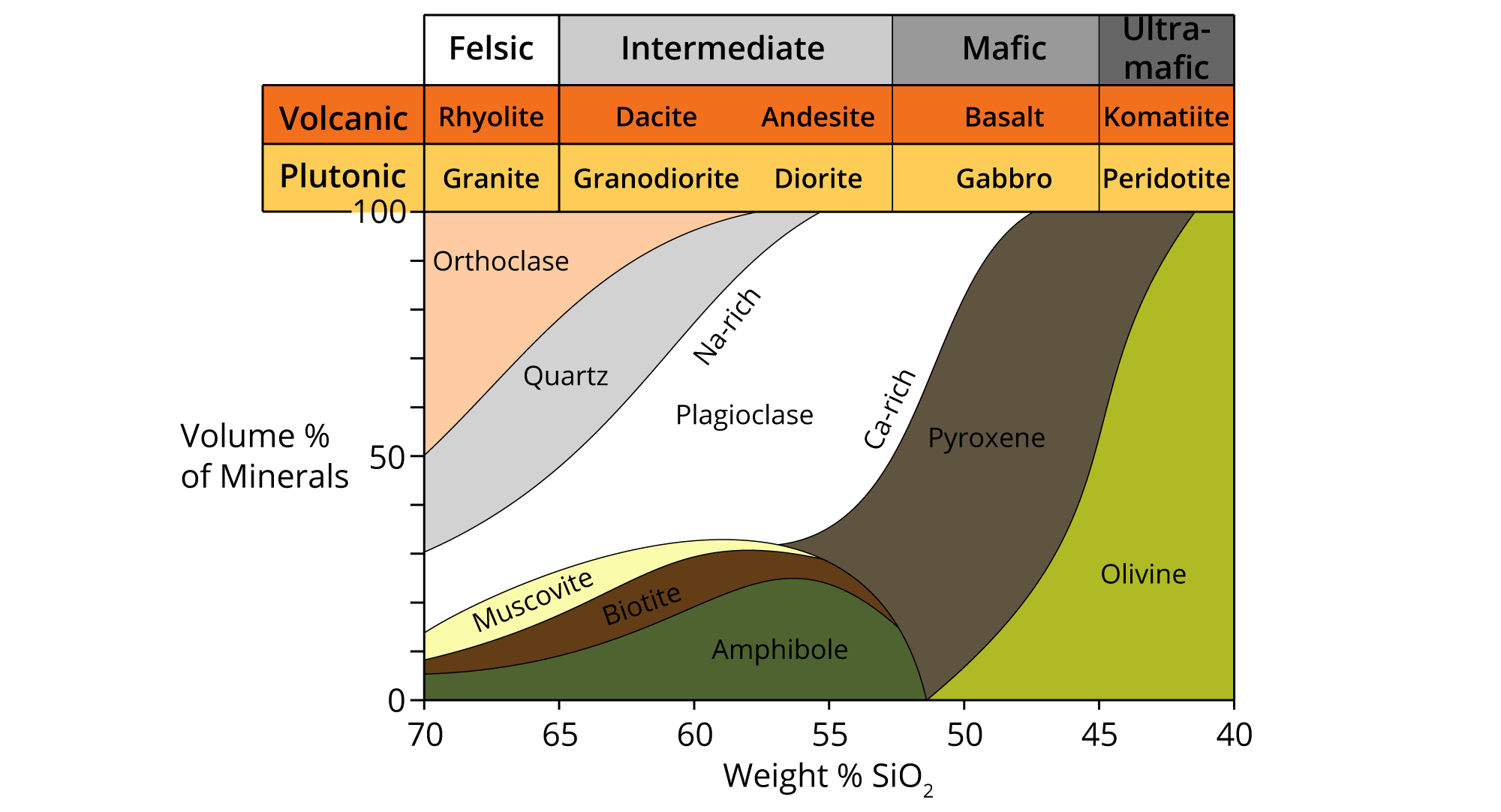
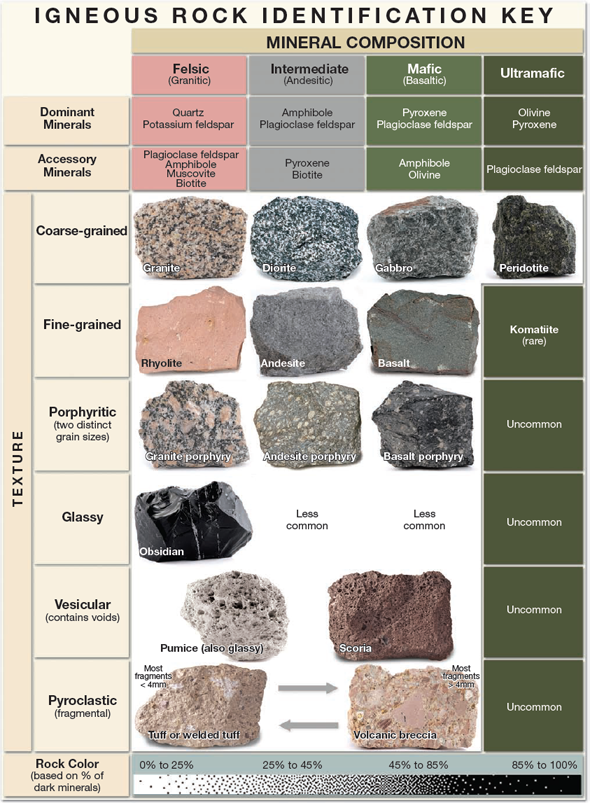
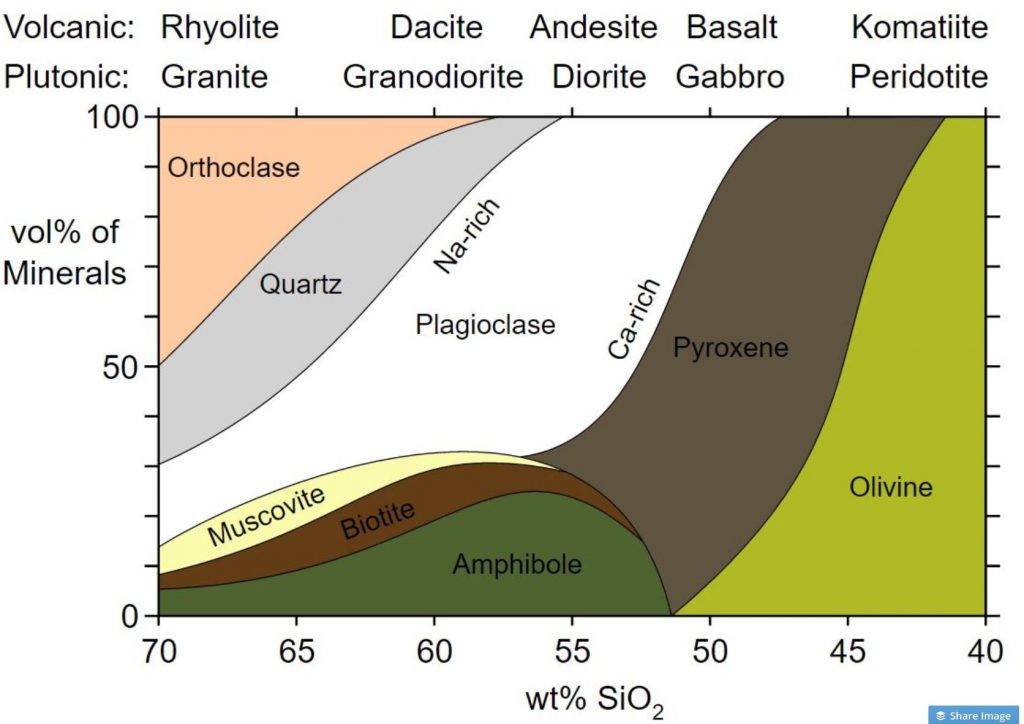
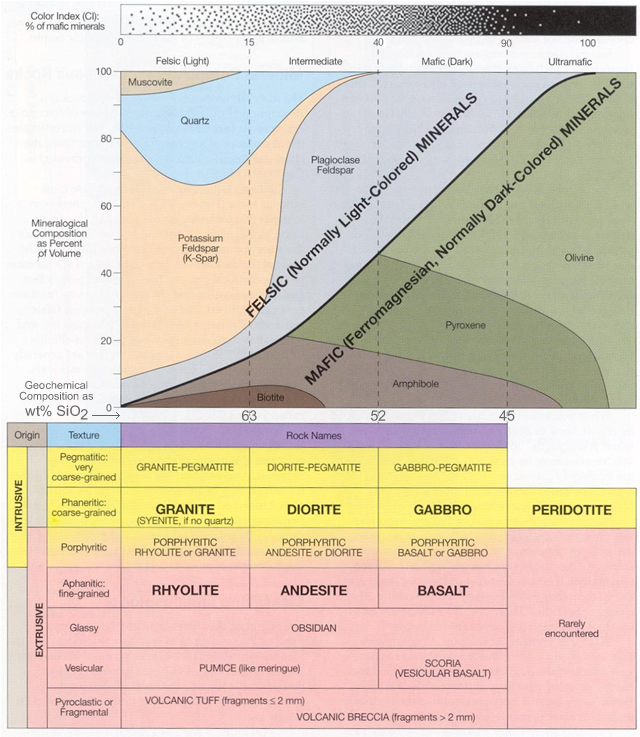
Igneous Rock Chart - This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. Diabase , diorite , gabbro , granite , pegmatite , and peridotite. Rocks rich in magnesium (mg) and iron (fe) tend to contain olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. This classification categorizes igneous rocks into four primary groups: In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 60% pyroxene and 40% olivine. Web figure 7.13 classification diagram for igneous rocks. A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. Rock types are plotted to show the relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase felspar they contain. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Rocks rich in magnesium (mg) and iron (fe) tend to contain olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Diabase , diorite , gabbro , granite , pegmatite , and peridotite. Here is how it works: A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. This classification categorizes igneous rocks into four primary groups: Web igneous rock charts. Web the diagram below shows the classification of intrusive igneous rocks in blue ridge parkway and the some of the different types of intrusive rocks beyond the three main types. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Composition refers to the rock’s specific mineralogy and chemical composition. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Igneous rocks are classified according to. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. This relates to the cooling. In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 60% pyroxene and 40% olivine. Web igneous rock charts. Web the classification of igneous rocks based on composition revolves around the silica (sio 2) content and the proportion of various minerals present in the rock. A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. Igneous rocks are. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. These minerals tend to be strongly. In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 60% pyroxene and. Web igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. These minerals tend to be strongly. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's. These minerals tend to be strongly. Rocks rich in magnesium (mg) and iron (fe) tend to contain olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. Composition refers to. Web the classification of igneous rocks based on composition revolves around the silica (sio 2) content and the proportion of various minerals present in the rock. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. The color of an igneous rock is related. Composition refers to the rock’s specific mineralogy and chemical composition. Web igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. Web the diagram below shows the classification of intrusive igneous rocks in blue ridge parkway and the some of the different types of intrusive rocks beyond the three main types. A given rock is represented by. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Here is how it works: Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: The color of an igneous rock is related to the colors of the minerals present. Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: These minerals tend to be strongly. Rock types are plotted to show the relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase felspar they contain. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Rocks rich in magnesium (mg) and iron (fe) tend to contain olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. Web the classification of igneous rocks based on composition revolves around the silica (sio 2) content and the proportion of various minerals present in the rock. In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: Rock types are plotted to show the relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase felspar they contain. Web igneous rock identification chart. Web igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. The color of an igneous rock is related to the colors of the minerals present. Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web the diagram below shows the classification of intrusive igneous rocks in blue ridge parkway and the some of the different types of intrusive rocks beyond the three main types. Web figure 7.13 classification diagram for igneous rocks.Igneous Rock Chart Flinn Scientific
Igneous Rock Types Chart
Igneous Rock Chart
Earth Science Lab Igneous Rock Identification Answers The Earth
Lani Aina Kai GG 103 Igneous Rock Classification Chart Geology
5.1 Classification of Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts
Igneous rock, Earth and space science, Igneous
Part A
General Classification of Igneous Rocks
PPT Igneous Rocks PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1540764
Felsic, Intermediate, Mafic, And Ultramafic.
In The Mafic Field, The Arrows Represent A Rock Containing 60% Pyroxene And 40% Olivine.
Diabase , Diorite , Gabbro , Granite , Pegmatite , And Peridotite.
Web Igneous Rocks Are Classified Based On Texture And Composition.
Related Post: