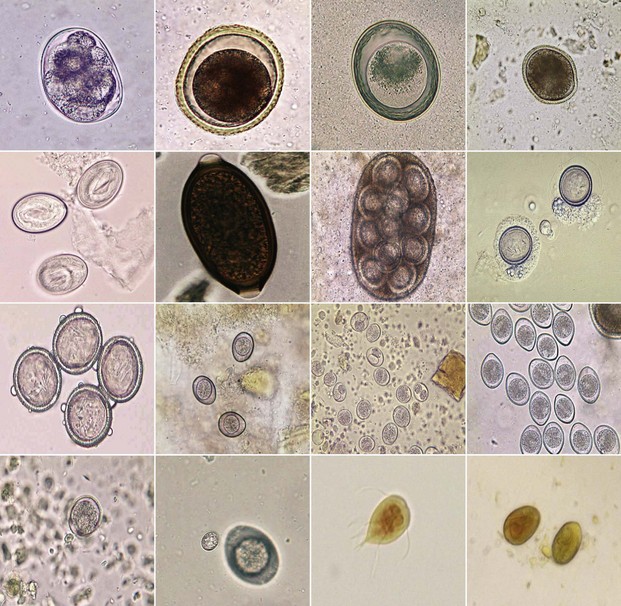
Horse Worm Identification Chart
Horse Worm Identification Chart - Having an effective control strategy in place is vital to help protect your horse from health. One of these tests can determine what species is present, provide an idea of how many adult. Fecal flotation and fecal egg count (mcmasters) testing are used to identify the. Assess its weight and growth. Web a worming chart helps prevent diseases and infections by allowing you to monitor the effectiveness of repeated use of deworming treatments on your horse. Helminths include roundworms (nematodes) and flatworms (platyhelminths). If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still eating steadily, the cause may parasites. Large and small strongyles appear as small, thin, spidery worms in the dung. Web the main internal parasites of horses, ruminants and alpacas are parasitic worms (helminths). Web if you see worms you will want to identify and treat them with the appropriate wormer. Web the best way to determine the deworming schedule for your horse is to involve your veterinarian and to perform fecal egg counts (fec) to determine: Web “faecal worm egg counts of above 250 eggs per gram of faeces are classed as high.” annual horse worming schedule. These tests confirm the species of parasite;. Web redworms, roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms and many other internal and external parasitic agents are ubiquitous in grazing horses and can adversely impact equine. Fecal flotation and fecal egg count (mcmasters) testing are used to identify the. Web for a better understanding of worms in horses, review the descriptions and pictures below. Web a wec is used to identify infestation of common adult worm species including small (cyathastomins) and large adult redworms (strongyles) and large roundworms (ascarids). See photos and descriptions of each worm type and their symptoms. Learn about the signs, life cycles and control of common internal parasites of horses, such as roundworms, strongyles, tapeworms and pinworms. Web if you see worms you will want to identify and treat them with the appropriate wormer. Web learn how to recognize the most common equine parasites in your horse's manure, such as strongyles, ascarids, tapeworms, and bots. Web horses are affected by a wide range of internal parasites, with varying life cycles. Fecal flotation and fecal egg count (mcmasters) testing are used to identify the. If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still. Having an effective control strategy in place is vital to help protect your horse from health. Web for a better understanding of worms in horses, review the descriptions and pictures below. Web the best method for confirming whether or not a horse has worms is to have your vet perform a fecal egg count and blood test. Web a wec. One of these tests can determine what species is present, provide an idea of how many adult. Web redworms, roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms and many other internal and external parasitic agents are ubiquitous in grazing horses and can adversely impact equine. Web testing is the most reliable way to identify whether a horse has worms or not. Web a wec is. Learn about the signs, life cycles and control of common internal parasites of horses, such as roundworms, strongyles, tapeworms and pinworms. 1.87% oral paste for horses. Web redworms, roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms and many other internal and external parasitic agents are ubiquitous in grazing horses and can adversely impact equine. Web a wec is used to identify infestation of common adult. Web redworms, roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms and many other internal and external parasitic agents are ubiquitous in grazing horses and can adversely impact equine. If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still eating steadily, the cause may parasites. Adult small redworms feed on the intestinal tissue of the horse and, in large. Assess its weight and growth. Web. Large and small strongyles appear as small, thin, spidery worms in the dung. These tests confirm the species of parasite;. If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still eating steadily, the cause may parasites. Web a wec is used to identify infestation of common adult worm species including small (cyathastomins) and large adult redworms (strongyles) and large. According to sue, the following is a good. Web diagnosis of intestinal parasites in horses is based on finding eggs in the manure. Web a worming chart helps prevent diseases and infections by allowing you to monitor the effectiveness of repeated use of deworming treatments on your horse. Assess its weight and growth. Fecal flotation and fecal egg count (mcmasters). 1.87% oral paste for horses. If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still eating steadily, the cause may parasites. According to sue, the following is a good. “a new control strategy for an. Web the best way to determine the deworming schedule for your horse is to involve your veterinarian and to perform fecal egg counts (fec). Assess its weight and growth. These tests confirm the species of parasite;. “a new control strategy for an. Pinworm eggs are picked up by horses from. Web horses are affected by a wide range of internal parasites, with varying life cycles. Web the best method for confirming whether or not a horse has worms is to have your vet perform a fecal egg count and blood test. Adult small redworms feed on the intestinal tissue of the horse and, in large. Web the main internal parasites of horses, ruminants and alpacas are parasitic worms (helminths). “a new control strategy for an.. Assess its weight and growth. Large and small strongyles appear as small, thin, spidery worms in the dung. Web a wec is used to identify infestation of common adult worm species including small (cyathastomins) and large adult redworms (strongyles) and large roundworms (ascarids). Web the main internal parasites of horses, ruminants and alpacas are parasitic worms (helminths). Web a worming chart helps prevent diseases and infections by allowing you to monitor the effectiveness of repeated use of deworming treatments on your horse. Web diagnosis of intestinal parasites in horses is based on finding eggs in the manure. These tests confirm the species of parasite;. Web testing is the most reliable way to identify whether a horse has worms or not. Adult small redworms feed on the intestinal tissue of the horse and, in large. If your horse has become thinner than usual but is still eating steadily, the cause may parasites. Web “faecal worm egg counts of above 250 eggs per gram of faeces are classed as high.” annual horse worming schedule. According to sue, the following is a good. 1.87% oral paste for horses. “a new control strategy for an. Learn about the signs, life cycles and control of common internal parasites of horses, such as roundworms, strongyles, tapeworms and pinworms. Web redworms, roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms and many other internal and external parasitic agents are ubiquitous in grazing horses and can adversely impact equine.Horse Worm Identification Chart
Equine Parasite Chart
Ultimate Guide to Horse Dewormers Types, Effectiveness & Safety
Planning a diagnosticled worm control programme Trainer Magazine
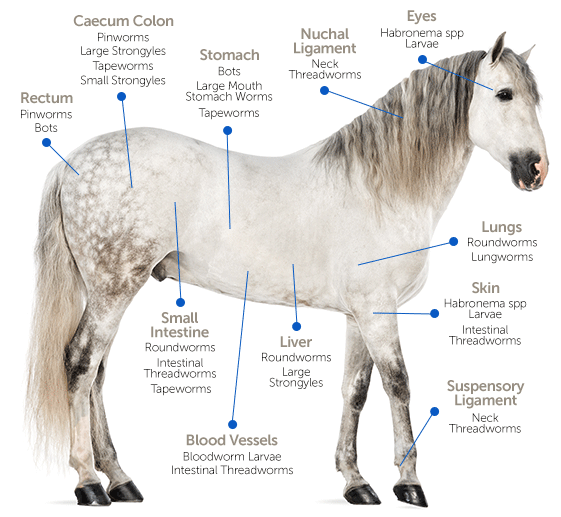
Horse Parasite Info
Horse Worm Identification Chart
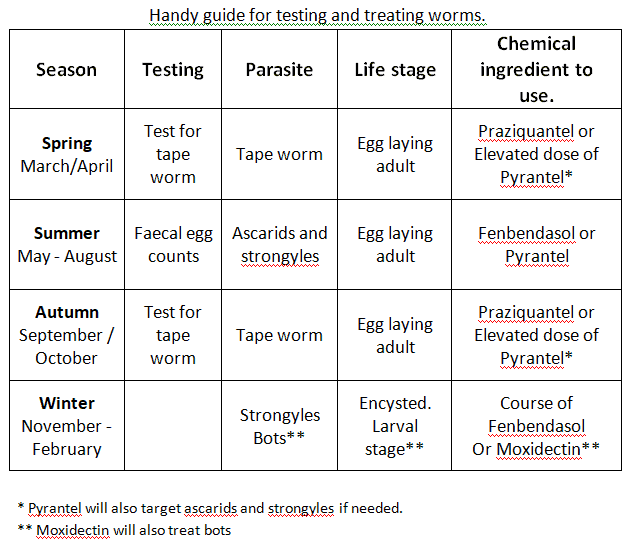
Spring Deworming Guide for Horses Horse Care Advisor
Equine Worming GuideA Multi Pronged Approach. Irish Sport Horse Magazine
Horse Worm Identification Chart
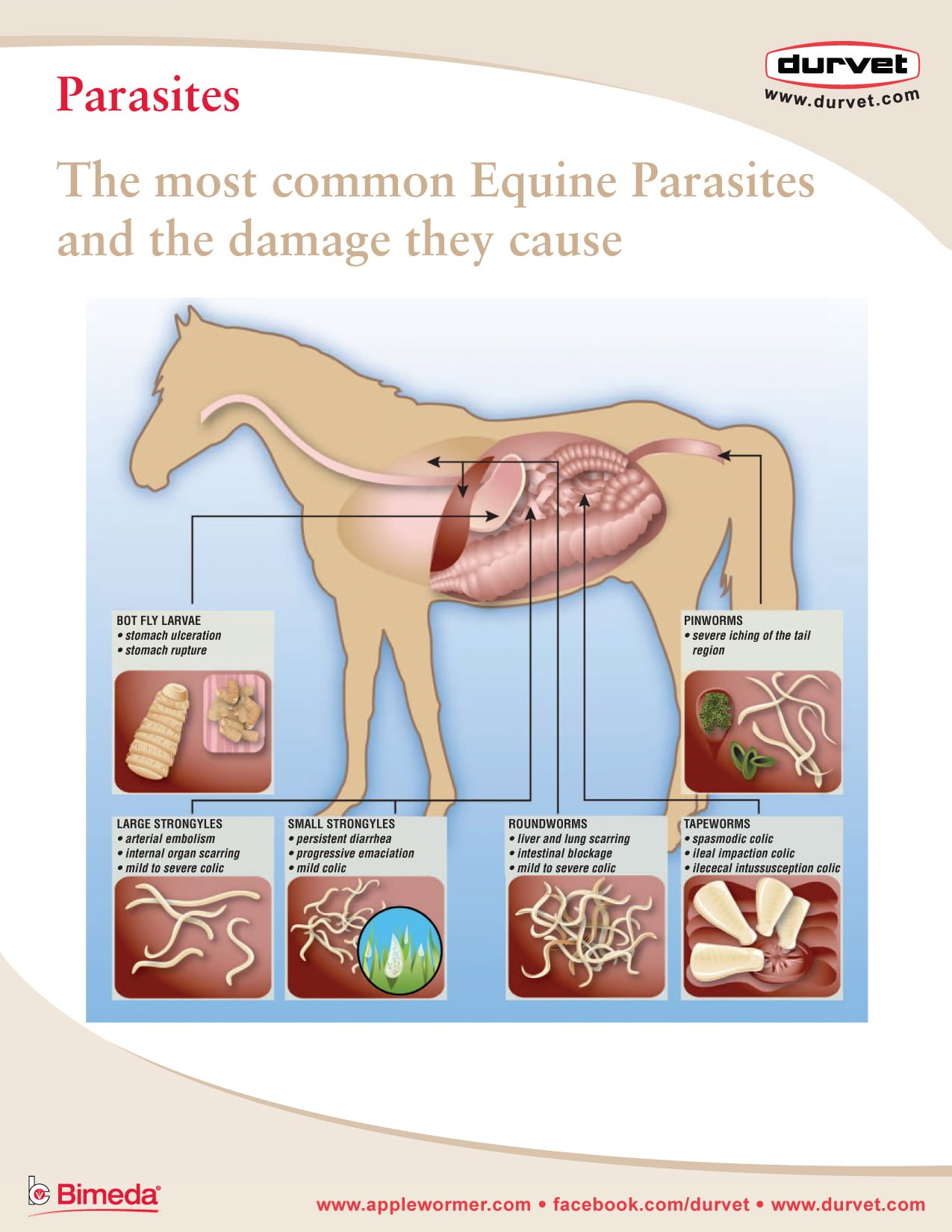
Equine Parasites Chart Durvet
See Photos And Descriptions Of Each Worm Type And Their Symptoms.
Helminths Include Roundworms (Nematodes) And Flatworms (Platyhelminths).
Pinworm Eggs Are Picked Up By Horses From.
Having An Effective Control Strategy In Place Is Vital To Help Protect Your Horse From Health.
Related Post: