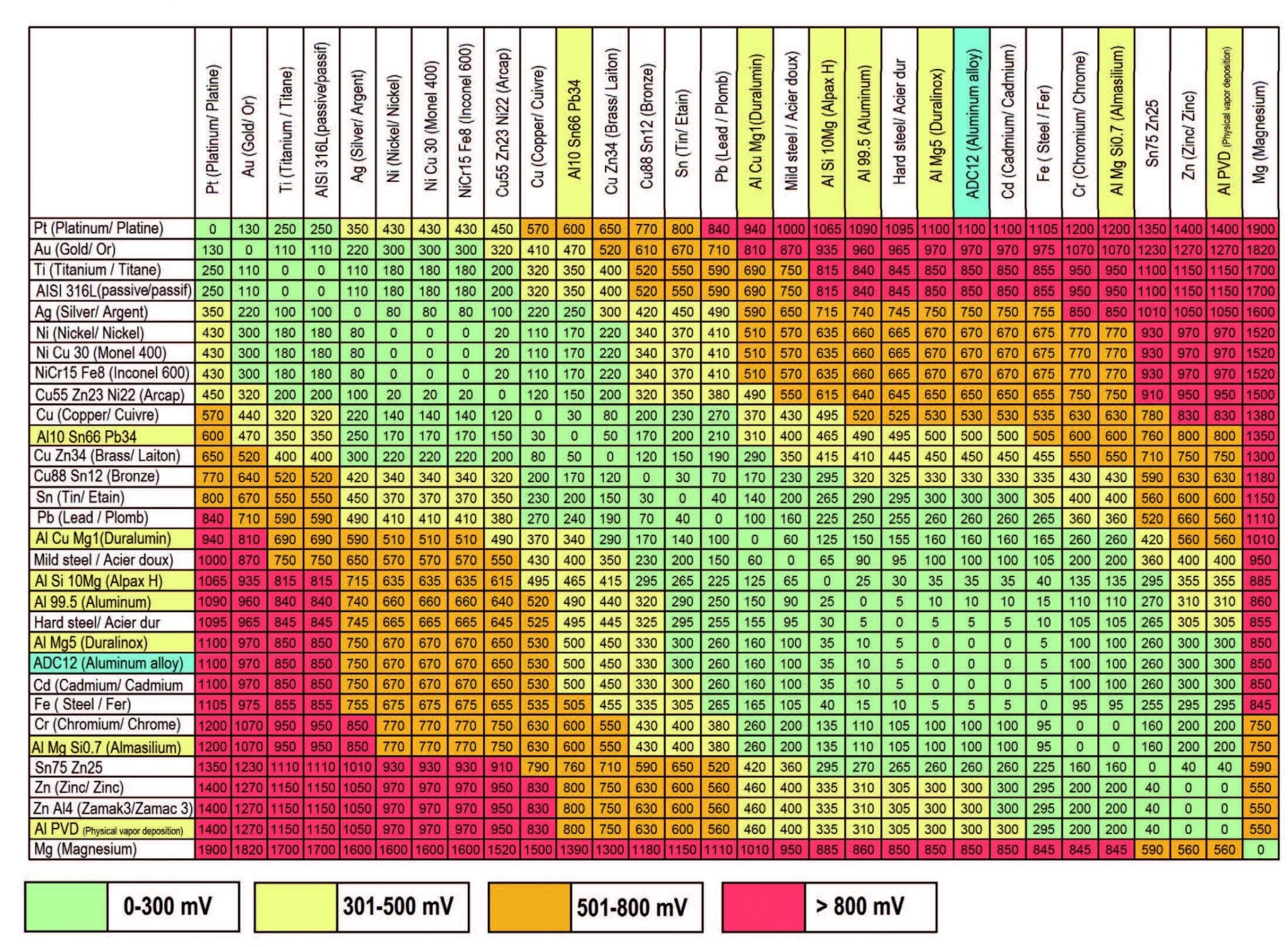
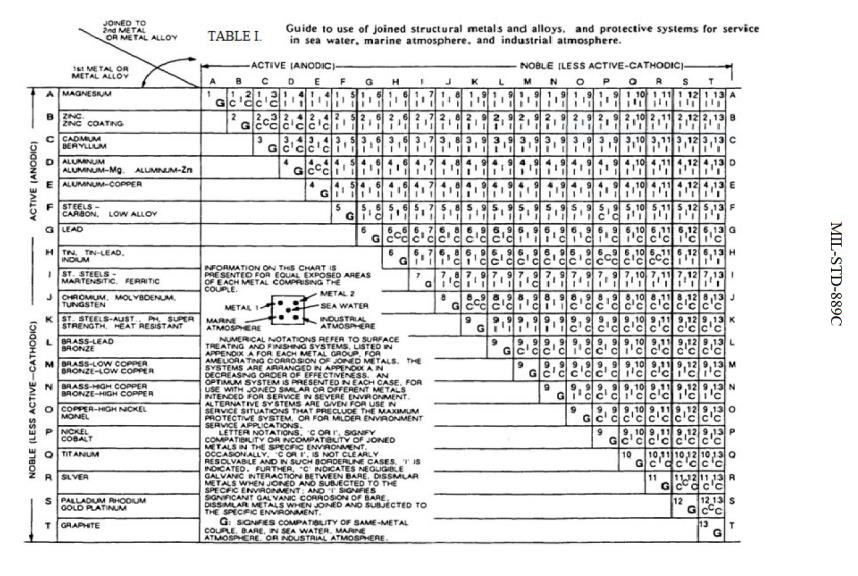
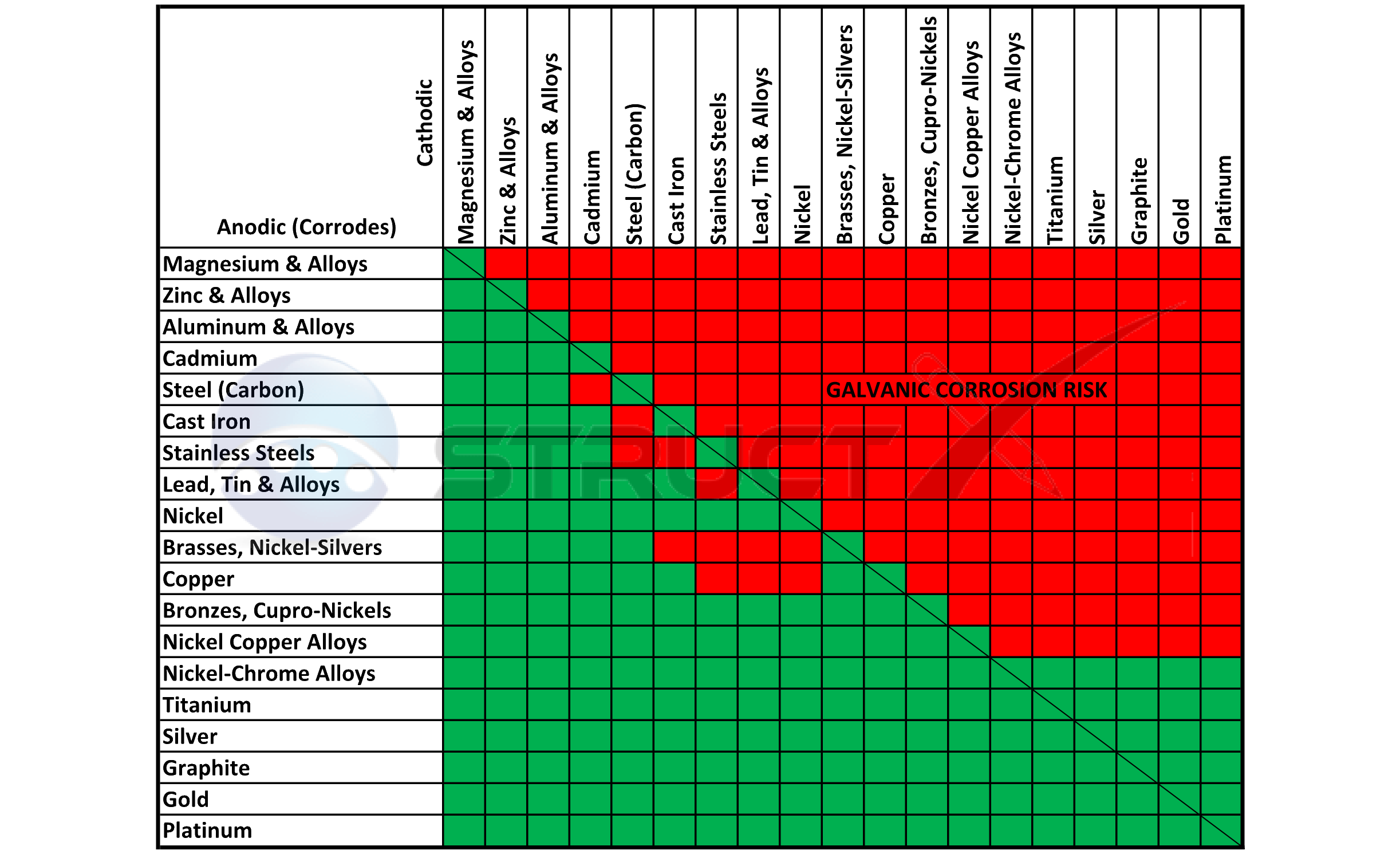
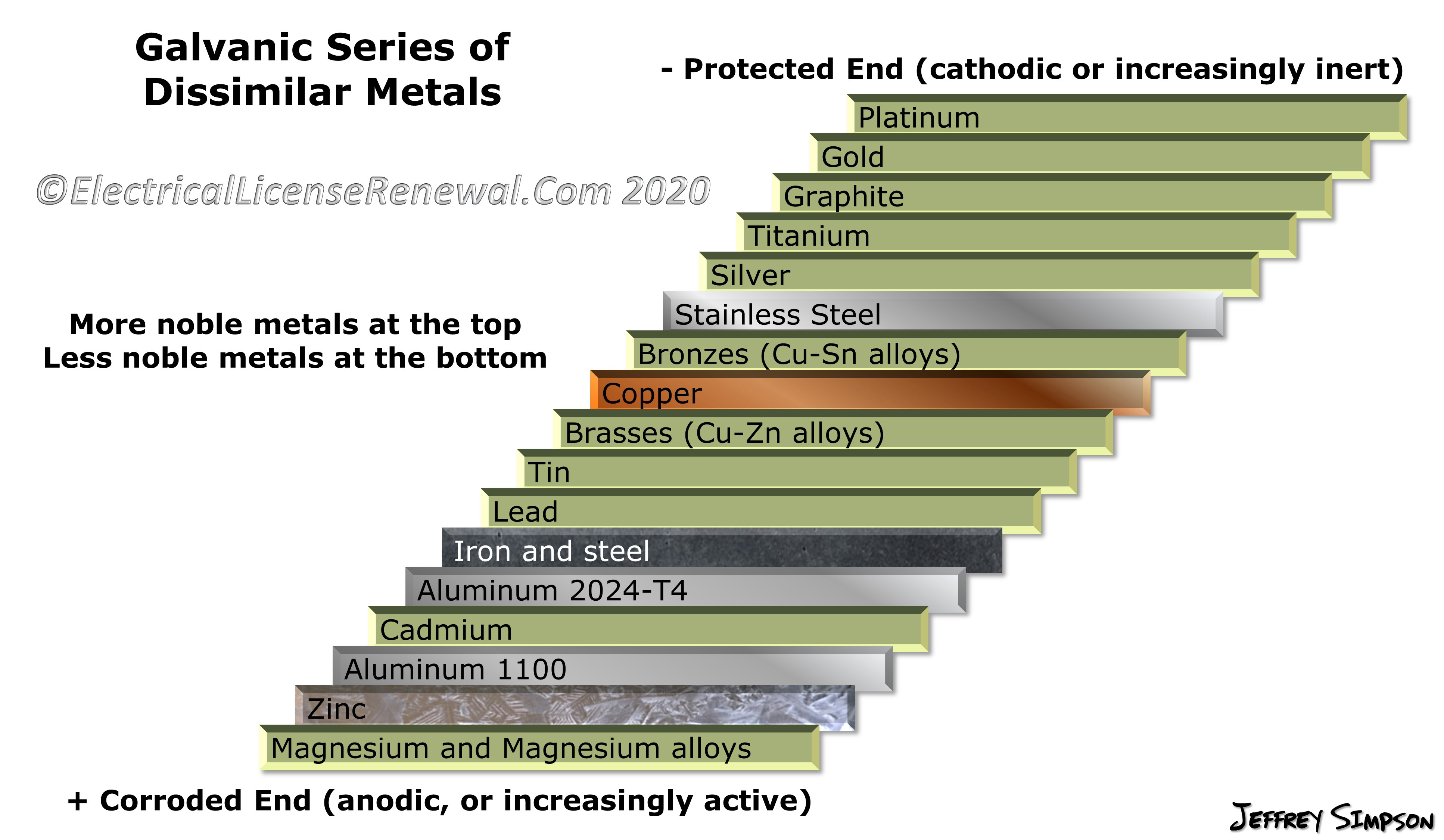
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion Chart
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion Chart - So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for. Web when design requires that dissimilar metals come in contact, galvanic compatibility can be managed by finishes and plating which protects the base materials from corrosion. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. Web this article examines how dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion typically attacks junction areas of dissimilar metals and occurs when the following three conditions are met. During this process, corrosion occurs on the anode, whereas. The chart shows the galvanic corrosion potential of various metals. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact electrically in the presence of an electrolyte. Web the susceptibility of different base metals to corrosion while in contact depends upon the difference between the contact potentials or the electromotive voltages of the metals. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals with different potentials are placed in electrical contact in an electrolyte. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs, and tips for avoiding it to prevent accidents and damaging project delays. Web this article examines how dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are coupled in a corrosive. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for. Web learn how to prevent galvanic corrosion (dissimilar metal corrosion) by understanding the three conditions that must exist for it to occur. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. For any combination of dissimilar metals, the metal with the lower number will act as an anode and will corrode. Web galvanic series, or nobility chart for dissimilar metals. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals with different potentials are placed in electrical contact in an electrolyte. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. If two different metals are placed in electrical contact and bridged by an electrolyte, a current figure 1: Web galvanic corrosion typically attacks junction areas of dissimilar metals. This phenomenon is named after italian ph… Find a table of anodic index values for. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs,. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are coupled in a corrosive. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different metals come in to contact. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of. Web learn how to prevent galvanic corrosion (dissimilar metal corrosion) by understanding the three conditions that must exist for it to occur. Find a table of anodic index values for. Web below is a. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs, and tips for avoiding it to prevent accidents and damaging project delays. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for. Web find out how dissimilar metals will corrode when placed against each other in an assembly using this chart. For any combination. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs, and tips for avoiding it to prevent accidents and damaging project delays. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different metals come in to contact. Web learn how to prevent galvanic corrosion (dissimilar metal corrosion) by understanding the three conditions that must exist for. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs, and tips for avoiding it to prevent accidents and damaging project delays. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for. If two different metals are placed in electrical contact and bridged by an electrolyte, a current figure 1: Web when design requires. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact electrically in the presence of an electrolyte. During this process, corrosion occurs on the anode, whereas. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of. This phenomenon is named after italian ph…. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact electrically in the presence of an electrolyte. Web learn how to prevent galvanic corrosion (dissimilar metal corrosion) by understanding the three conditions that must exist for it to occur. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web when design requires that dissimilar metals. During this process, corrosion occurs on the anode, whereas. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact electrically in the presence of an electrolyte. Web learn how to prevent galvanic corrosion (dissimilar metal corrosion) by understanding the three conditions that must exist for it to occur. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different. Web when design requires that dissimilar metals come in contact, galvanic compatibility can be managed by finishes and plating which protects the base materials from corrosion. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different metals come in to contact. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals with different potentials are placed in electrical contact in an electrolyte. Find a table of anodic index values for. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of. The chart shows the galvanic corrosion potential of various metals. Web the susceptibility of different base metals to corrosion while in contact depends upon the difference between the contact potentials or the electromotive voltages of the metals. Web below, we delve into dissimilar metal corrosion, how and why it occurs, and tips for avoiding it to prevent accidents and damaging project delays. Web find out how dissimilar metals will corrode when placed against each other in an assembly using this chart. During this process, corrosion occurs on the anode, whereas. It may also take place with one metal with. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact electrically in the presence of an electrolyte. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. If two different metals are placed in electrical contact and bridged by an electrolyte, a current figure 1: For any combination of dissimilar metals, the metal with the lower number will act as an anode and will corrode. It includes a chart that shows how different plating materials react to one another with.FAQ 1 Galvanic/Dissimilar Metal Corrosion
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion Chart
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals A Visual Reference of
Dissimilar metal corrosion with chemical filmed (Alodine, Iridite
Dissimilar joining of Al with steel? r/Welding
Stainless Steel Galvanic Corrosion Chart
Dissimilar Corrosion Materials Tables
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals
Dissimilar Metals Corrosion Chart
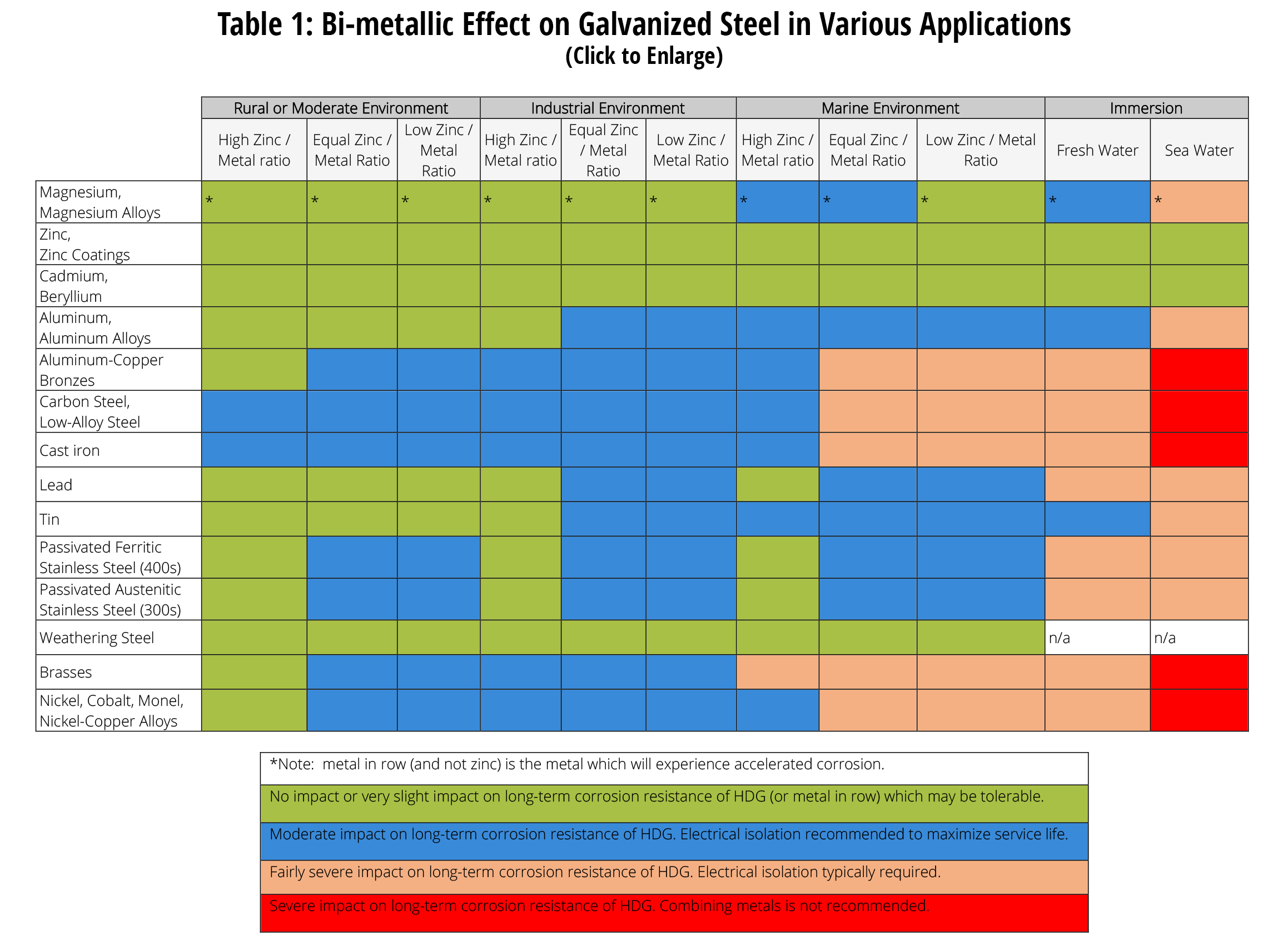
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion with… American Galvanizers Association
Web Galvanic Corrosion (Also Called ' Dissimilar Metal Corrosion' Or Wrongly 'Electrolysis') Refers To Corrosion Damage Induced When Two Dissimilar Materials Are Coupled In A Corrosive.
A Similar Galvanic Reaction Is Exploited In Primary Cells To Generate A Useful Electrical Voltage To Power Portable Devices.
So, For Example, Choosing Zinc On Zinc Would Have The Lowest Risk For.
Galvanic Corrosion (Also Called Bimetallic Corrosion Or Dissimilar Metal Corrosion) Is An Electrochemical Process In Which One Metal Corrodes Preferentially When It Is In Electrical Contact With Another, In The Presence Of An Electrolyte.
Related Post: