Bond Energies Chart
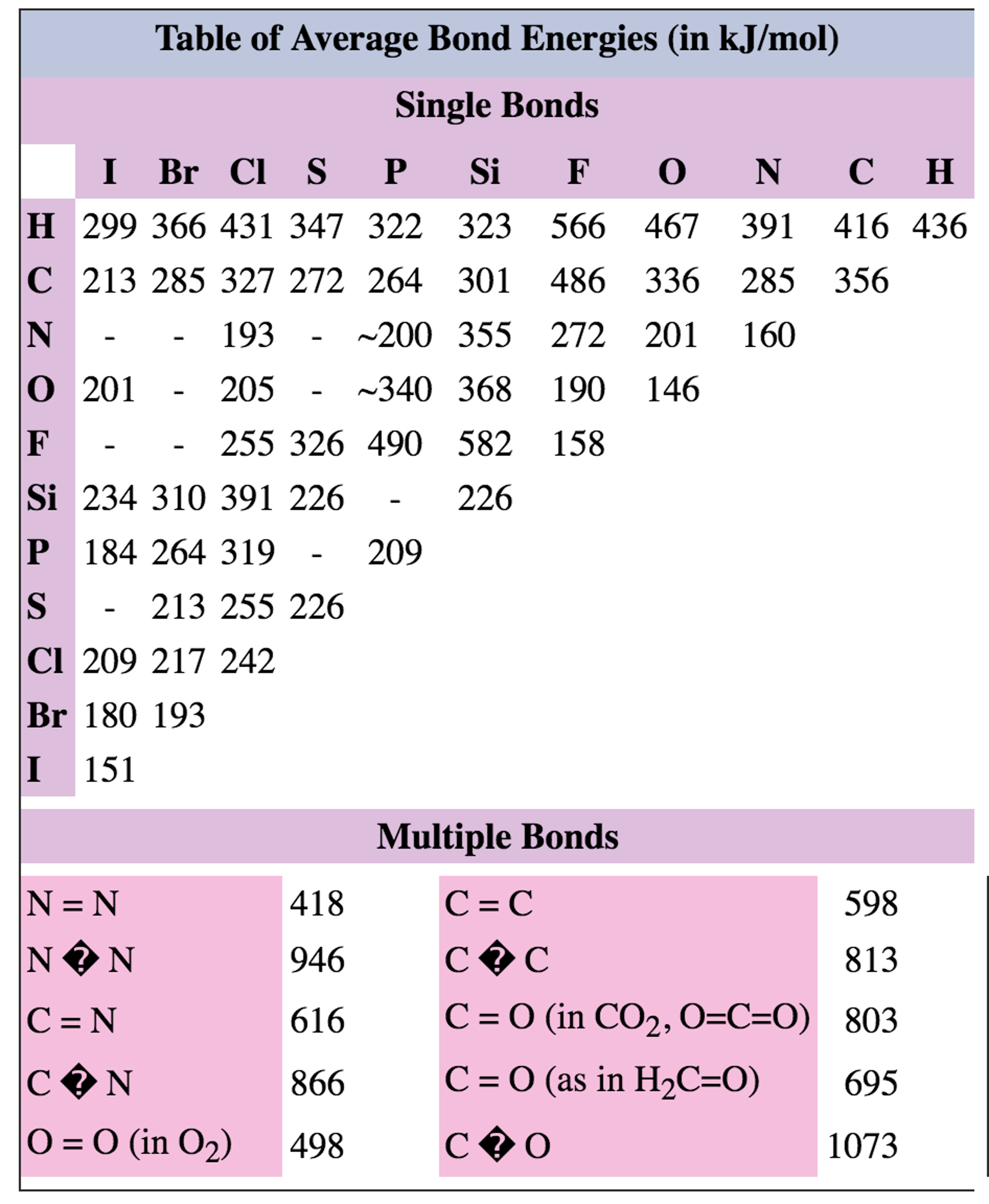
Bond Energies Chart - Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. To define and used average bond energies. Web this page has tables of standard bond energies and bond dissociation energies. Various qualities determine a bond’s dissociation and formation energies. Web the energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. Bond enthalpies are essentially a measure of how strong a covalent bond is. Cottrell, the strengths of chemical bonds, 2nd ed., butterworths, london, 1958; We often use a more condensed form of bond energy tables as shown below. We can calculate a more general bond energy by finding the average of the bond energies of a specific bond in different molecules to get the average bond energy. When a bond is formed between two atoms, energy is released. Bond strength qualities and periodic trends. Use the bond energies from the table to calculate an approximate δh 0rxn for the following equation: Calculate the heat of combustion, for c 2 h 6 using the bond dissociation energies in the table. Web the average bond energy is therefore +1662/4 kj, which is +415.5 kj per mole of bonds. Bond enthalpies are essentially a measure of how strong a covalent bond is. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. So, ‘’the bond energy is the average amount of energy required to break all bonds of a particular type in one mole of the substance’’. The exact bond enthalpy of a particular chemical bond depends upon the molecular environment in which the bond exists. Web the energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. To define and used average bond energies. Cottrell, the strengths of chemical bonds, 2nd ed., butterworths, london, 1958; Web the average bond energy is therefore +1662/4 kj, which is +415.5 kj per mole of bonds. 2 nh 3 (g) + cl 2 (g) → n 2 h 4 (g) + 2 hcl (g) exercise 2. The same amount of energy is absorbed when the bond is broken. The exact bond enthalpy of a particular chemical bond depends upon the molecular environment in which the bond exists. Web atoms are held together by a certain amount of energy called bond energy. We often use a more condensed form of bond energy tables as shown below. Web average bond energies *bond dissociation energies for diatomic molecules can be directly. We can calculate a more general bond energy by finding the average of the bond energies of a specific bond in different molecules to get the average bond energy. Evaluate enthalpies of reactions using bond energies. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. Web table. Web table shows energy of common chemical bonds in selected unit (kj/mol, atomic units, ev etc.). Values are in kj/mol of bonds. Define bond length and bond energy and note the relationship between the two. Explain its relationship to bond length or bond energy. The rest are average bond energies. The same amount of energy is absorbed when the bond is broken to form neutral atoms. Chemical processes are labeled as exothermic or endothermic based on whether they give off or absorb energy, respectively. Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. Most commonly, a bond’s strength depends on: The following tables list experimental bond dissociation enthalpies. Evaluate enthalpies of reactions using bond energies. This is typically the types of tables that are put on exams to save space. Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. Web this equation can solve for any of these three values and is a key formula in thermodyanamics, physical chemistry, and more. 2 nh 3 (g) +. We can calculate a more general bond energy by finding the average of the bond energies of a specific bond in different molecules to get the average bond energy. Bond strength qualities and periodic trends. * average bond dissociation enthalpies in kcal per mole (there can be considerable variability in some of these values.) The following tables list experimental bond. Evaluate enthalpies of reactions using bond energies. * average bond dissociation enthalpies in kcal per mole (there can be considerable variability in some of these values.) This is typically the types of tables that are put on exams to save space. So, ‘’the bond energy is the average amount of energy required to break all bonds of a particular type. Web atoms are held together by a certain amount of energy called bond energy. Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. Bond enthalpies are essentially a measure of how strong a covalent bond is. This is typically the types of tables that are put on exams to save space. Web the bond energy is a measure. Chemical processes are labeled as exothermic or endothermic based on whether they give off or absorb energy, respectively. Values are in kj/mol of bonds. Web average bond energies *bond dissociation energies for diatomic molecules can be directly measured. Web properties of atoms, radicals, and bonds 4.41 table 4.11 bond dissociation energies the bond dissociation energy (enthalpy change) for a bond. Web properties of atoms, radicals, and bonds 4.41 table 4.11 bond dissociation energies the bond dissociation energy (enthalpy change) for a bond a 9b which is broken through the reaction ab : Bond energies are also called bond enthalpies, and in the past have been known as bond strengths. The same amount of energy is absorbed when the bond is broken to form neutral atoms. Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. Calculate the heat of combustion, for c 2 h 6 using the bond dissociation energies in the table. Define bond length and bond energy and note the relationship between the two. Web from this graph, we can determine the equilibrium bond length (the internuclear distance at the potential energy minimum) and the bond energy (the energy required to separate the two atoms). * average bond dissociation enthalpies in kcal per mole (there can be considerable variability in some of these values.) The si units used to describe bond energy is kilojoules per mole of bonds (kj/mol). Web the bond energy is a measure of the amount of energy needed to break apart one mole of covalently bonded gases. The exact bond enthalpy of a particular chemical bond depends upon the molecular environment in which the bond exists. Web table shows energy of common chemical bonds in selected unit (kj/mol, atomic units, ev etc.). Recognize covalent substances and characterize ionic character as difference in electronegativity. Web the energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. Bond strength qualities and periodic trends. Evaluate enthalpies of reactions using bond energies.The Heat of Reaction from Bond Dissociation Energies Chemistry Steps
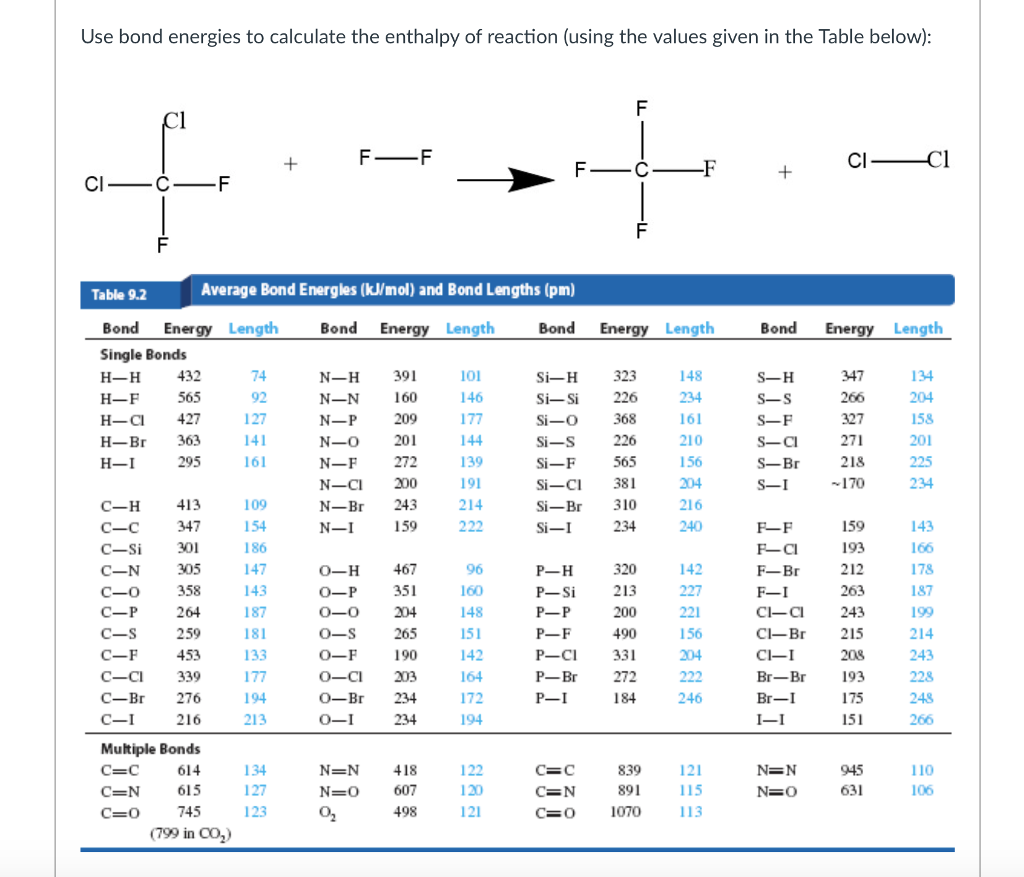
[Solved] Using the appropriate bond energies, calculate the heat of
Bond Energies Chart
Bond Energies Chart
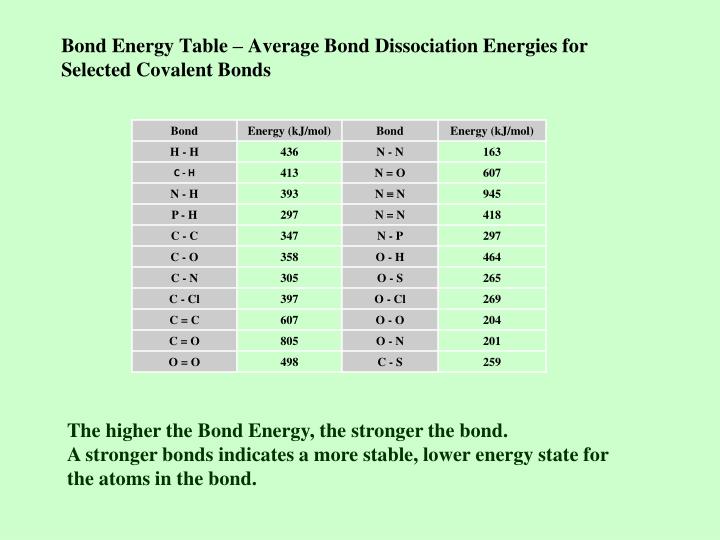
Average Bond Energies Chart
Bond Length and Bond Energy
Bond Length and Bond Strength Pathways to Chemistry
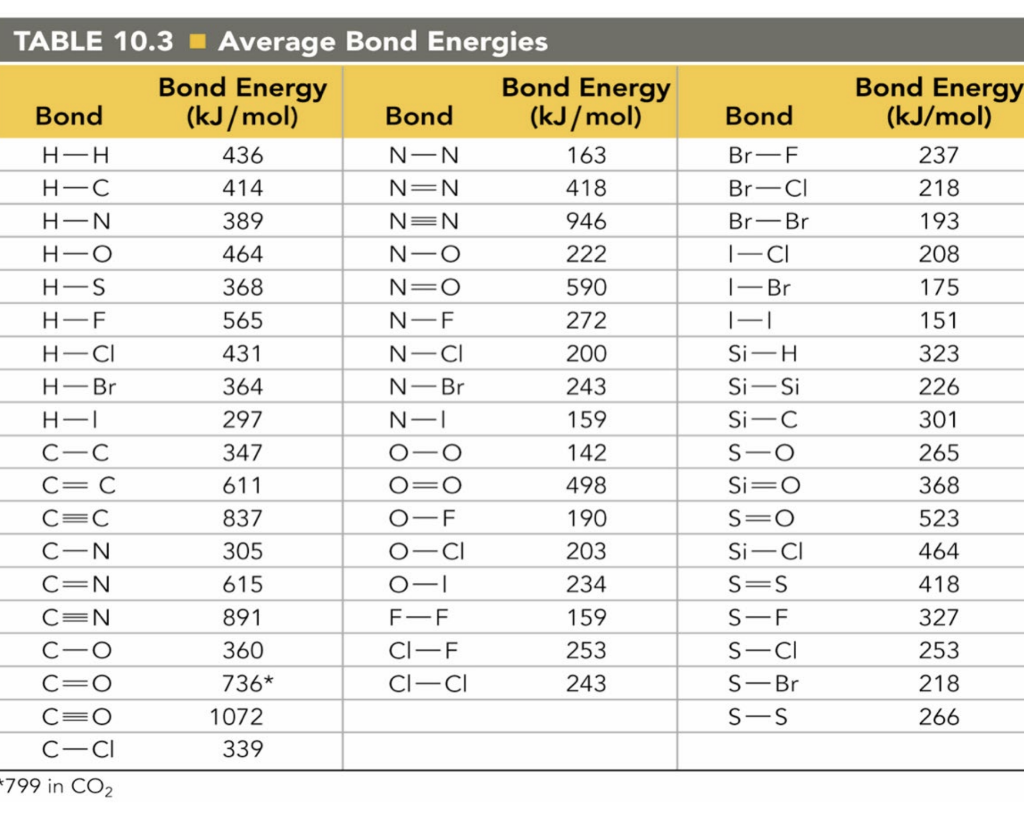
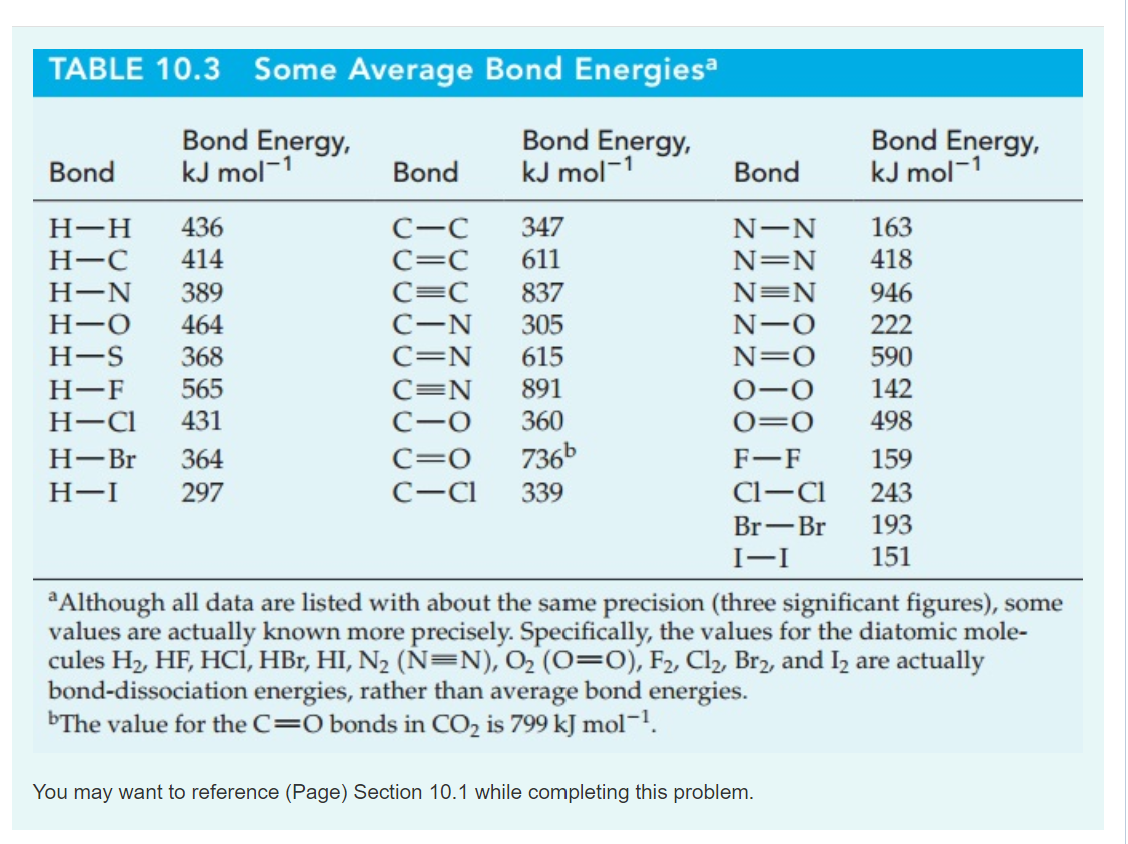
Solved Bond TABLE 10.3 Average Bond Energies Bond Energy
Table Of Bond Energies Pathways To Chemistry vrogue.co
Bond Energy Profile Chart
You Can Take All These Terms As Meaning The Same Thing.
So, ‘’The Bond Energy Is The Average Amount Of Energy Required To Break All Bonds Of A Particular Type In One Mole Of The Substance’’.
We Often Use A More Condensed Form Of Bond Energy Tables As Shown Below.
Web Average Bond Energies *Bond Dissociation Energies For Diatomic Molecules Can Be Directly Measured.
Related Post:


.PNG)