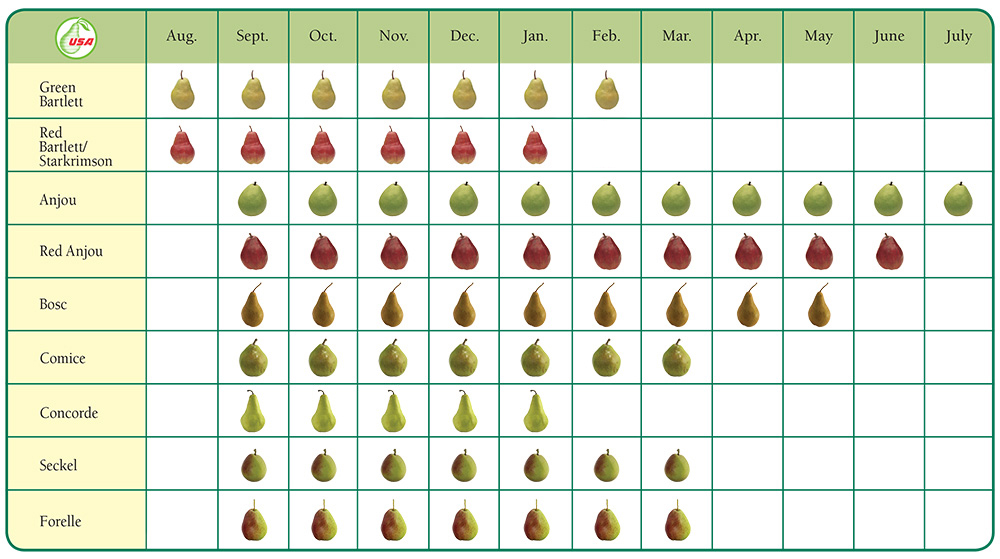
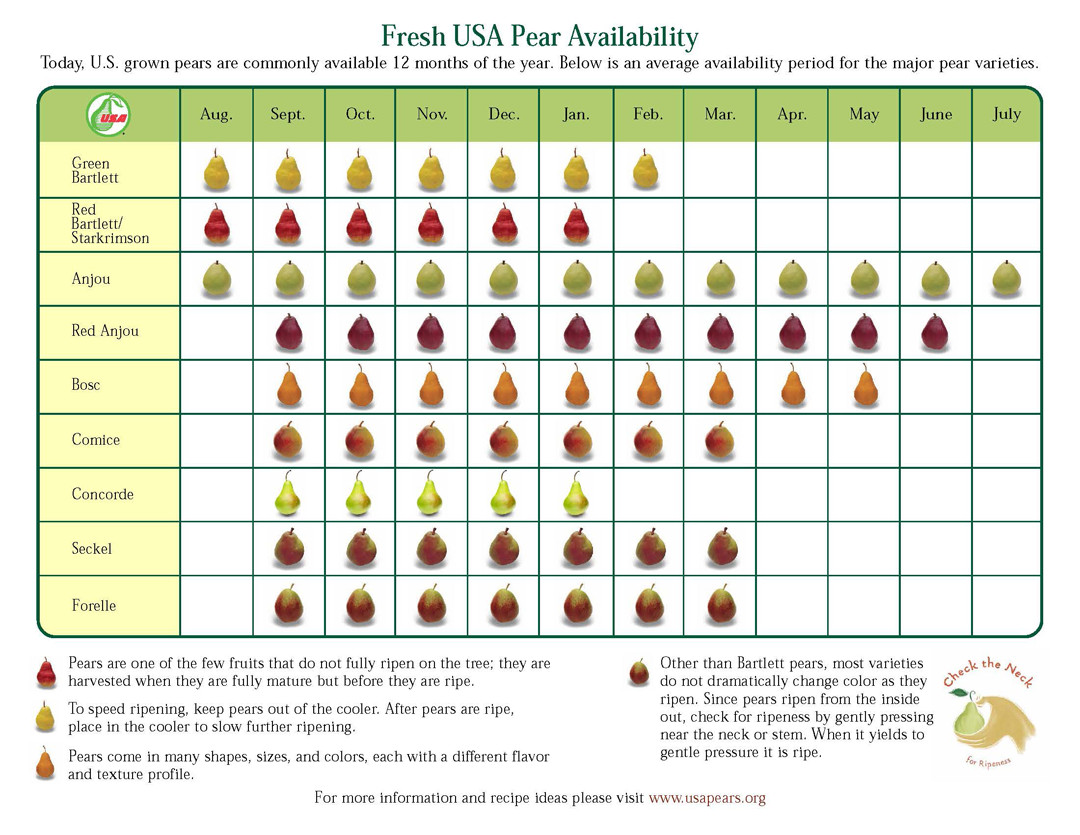
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Ripening Chart - When the estimated ripeness date is near, pick a pear and taste it! Web check the color of the pear. It shouldn’t manifest many brown spots and should give off a sweet fragrance with a bouncy feel. This quick and easy method will help you select the best pears from the produce aisle. The color should be mostly even all over the pear, not in spots. To identify a ripe asian pear, you can check its skin, feel the weight, smell it, check the texture, or ask for a sample. They can also be preserved by either canning or drying. Web although asian pears bruise easily, excessive brown spots indicate a pear that is over ripe. European pears are represented in green, while asian varieties stand out in yellow. The asian pear tree ( pyrus pyrifolia) is in the rosaceae family tree, like plums and peaches, and is a prolific tree, producing many fruits each season. Learn essential techniques for determining the perfect ripeness of asian pears, empowering your fruit selection and culinary endeavors. If left on the tree, pears ripen from the inside out and, by the time they seem to be at the ripe stage, they are beyond it — usually mushy with a mealy texture beneath the skin. Web while most types of fruit reach their peak on the branch or vine, pears need to be picked before ripening. Web asian pear trees can take between three to five years to begin producing fruit after propagation. Web although asian pears bruise easily, excessive brown spots indicate a pear that is over ripe. They ripen on the tree and maintain a crisp, juicy texture. Once picked, the fruits will not ripen further. It shouldn’t manifest many brown spots and should give off a sweet fragrance with a bouncy feel. Web look for a shift in color from green to yellow or brown on the asian pears as they ripen fully on the tree. Web asian pear trees bloom in the spring, usually in april or may. By growing your own, you can decide when the fruit has reached peak flavor. Web asian pears can be harvested near ripe and sold immediately for the fresh market. Store the fruit at room temperature, out of direct sunlight if. Web can you ripen an asian pear after picking? A handy guide to help you choose pear varieties according to. Web how to tell if an asian pear is ripe? They can also be preserved by either canning or drying. If you twist any asian pears, they should easily detach off the branch. Web although asian pears bruise easily, excessive brown spots indicate a pear that is over ripe. Web color changes are important to deciding when asian pears are. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. Learn essential techniques for determining the perfect ripeness of asian pears, empowering your fruit selection and culinary endeavors. Like apples, each fruit contains five seeds. Web color changes are important to deciding when asian pears are ripe. They can also be preserved by either canning or drying. Also find out when the best time of year is to buy them. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. Web unlike some fruits that continue to ripen after picking, asian pears reach their peak ripeness while still on the tree. Learn essential techniques for determining the perfect ripeness of asian pears, empowering your fruit selection and culinary. This quick and easy method will help you select the best pears from the produce aisle. It shouldn’t manifest many brown spots and should give off a sweet fragrance with a bouncy feel. They ripen on the tree and maintain a crisp, juicy texture. Web the spruce / steven merkel. Web how to tell if an asian pear is ripe? The flowers are white and fragrant. It shouldn’t manifest many brown spots and should give off a sweet fragrance with a bouncy feel. The asian pear tree ( pyrus pyrifolia) is in the rosaceae family tree, like plums and peaches, and is a prolific tree, producing many fruits each season. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. Learn. Web this chart will help you choose varieties of peach, nectarine and apricot by ripening and maturity period. Gently twist a fruit to see whether it’s mature. Web asian pears, unlike european pears, should be allowed to ripen on the tree. Web how to tell if an asian pear is ripe? The asian pear tree ( pyrus pyrifolia) is in. Like apples, each fruit contains five seeds. Store the fruit at room temperature, out of direct sunlight if. When the estimated ripeness date is near, pick a pear and taste it! Generally speaking, your asian pears are ready to pick when they begin falling from the tree. Web asian pears are usually picked ripe and ready to eat. Kosui, shinseiki, chojuro, ichiban, hamese. Web the spruce / steven merkel. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. Web how to tell if an asian pear is ripe? Learn essential techniques for determining the perfect ripeness of asian pears, empowering your fruit selection and culinary endeavors. Kosui, shinseiki, chojuro, ichiban, hamese. The asian pear tree ( pyrus pyrifolia) is in the rosaceae family tree, like plums and peaches, and is a prolific tree, producing many fruits each season. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. Web the spruce / steven merkel. Web if you want to pick a perfect pear every time, here's how. Once picked, the fruits will not ripen further. Web learn all you ever wanted to know about asian pears from when they are ripe to eat to what makes them different than other types of pears. Gently twist a fruit to see whether it’s mature. More than five or six, and the pear is likely over ripe or severely bruised. Shinko, hosui, yoinashi, 20th century (nijisseiki) asian pear tree. A handy guide to help you choose pear varieties according to their ripening and maturity periods. The flowers are white and fragrant. Web the pear ripening chart is a visual tool that tracks the maturity progression of various pear varieties throughout the season. The asian pear tree ( pyrus pyrifolia) is in the rosaceae family tree, like plums and peaches, and is a prolific tree, producing many fruits each season. If you twist any asian pears, they should easily detach off the branch. Web check the color of the pear. Communis ), asian varieties don’t turn soft and mushy when ripe. This quick and easy method will help you select the best pears from the produce aisle. Web asian pear trees bloom in the spring, usually in april or may. In fact, they will not ripen properly if left on the tree. Kosui, shinseiki, chojuro, ichiban, hamese.Pear Ripening Chart When Are Pears In Season
PBNW Retailer Training Course 1
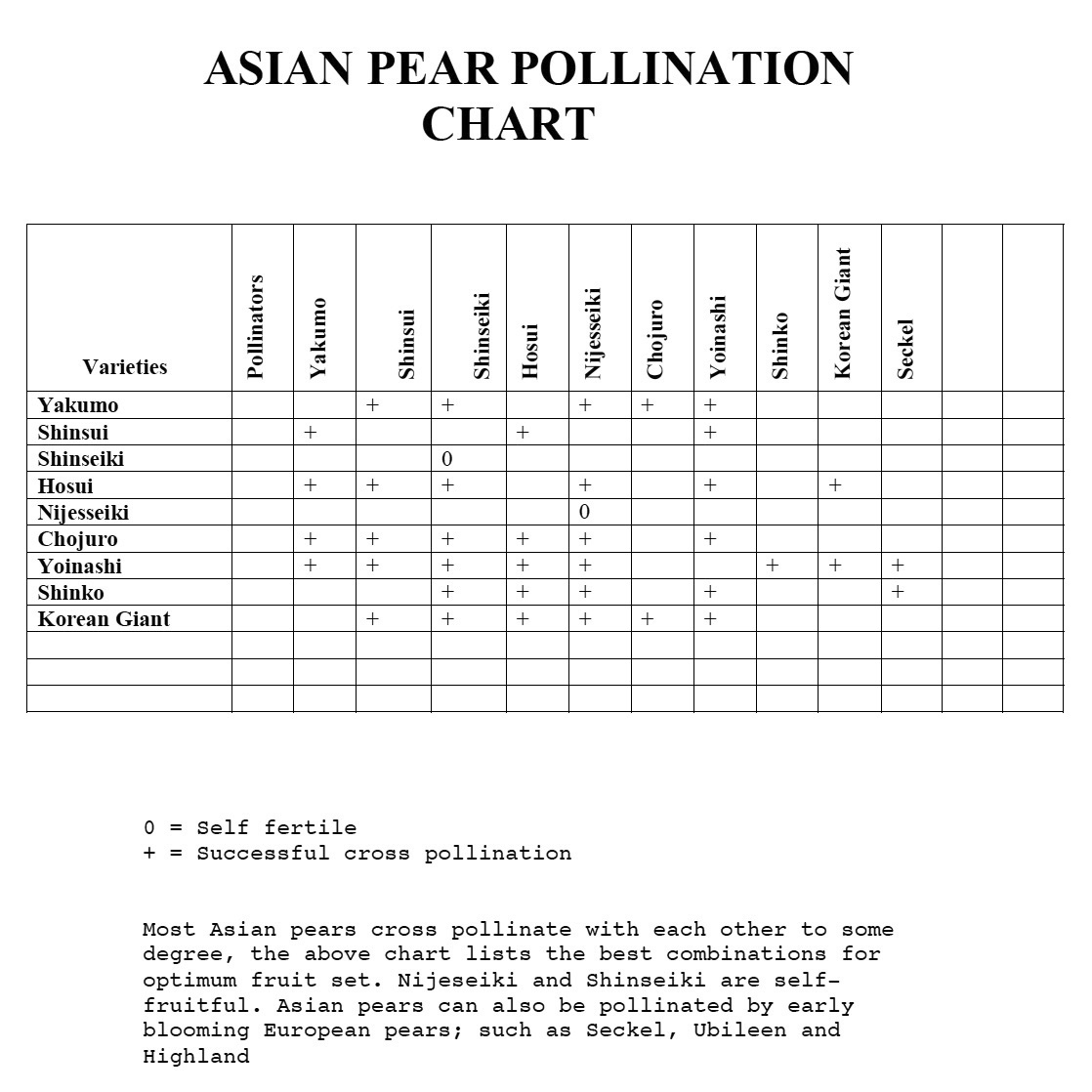
Asian Pear Pollination Charts AgriHunt
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Pollination Chart
Asian Pear Ripening Chart
Asian Pear Pollination Chart
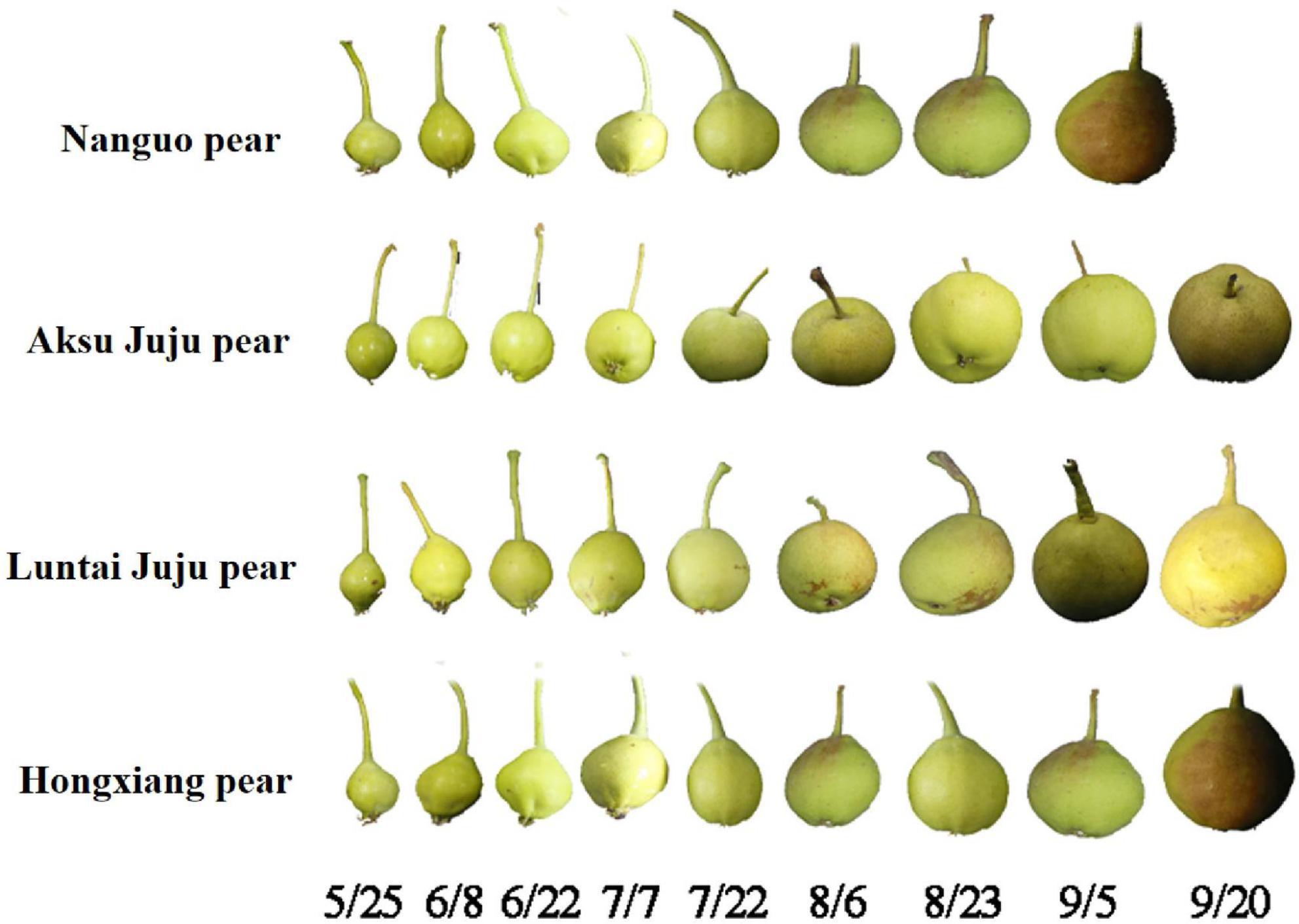
Web Color Changes Are Important To Deciding When Asian Pears Are Ripe.
To Identify A Ripe Asian Pear, You Can Check Its Skin, Feel The Weight, Smell It, Check The Texture, Or Ask For A Sample.
The Fruit Ripens In The Fall, Usually In September Or October.
Some Varieties Never Change Color, While Others Change From Green To Brown Or Green To Yellow.
Related Post: